Python列表去重的4种方式及性能对比
大家好,欢迎来到 Crossin的编程教室 !
列表去重是Python中一种常见的处理方式,任何编程场景都可能会遇到需要列表去重的情况。
列表去重的方式有很多,本文将讲解其中较为常见的4种,并进行性能的对比。
让我们先制造一些简单的数据,生成0到99的100万个随机数:
from random import randrangeDUPLICATES = [randrange(100) for _ in range(1000000)]
接下来尝试这4种去重方式中最简单直观的方法:
1.新建一个数组,遍历原数组,如果值不在新数组里便加入到新数组中。
# 第一种方式def easy_way():unique = []for element in DUPLICATES:if element not in unique:unique.append(element)return unique
进入ipython使用timeit计算其去重耗时:
timeit easy_way()1.16 s ± 137 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
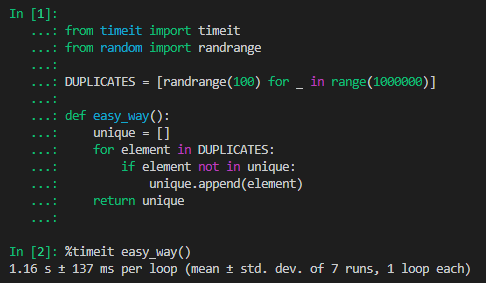
平均耗时在1.16秒左右,但是在这个例子中我们使用了数组作为存储对象,实际上如果我们改成集合存储去重后的结果,性能会快不少:
def easy_way():unique = set()for element in DUPLICATES:if element not in unique:unique.add(element)return unique
timeit easy_way()48.4 ms ± 11.6 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
平均耗时在48毫秒左右,改善明显,这是因为集合和数组的内在数据结构完全不同,集合使用了哈希表,因此速度会比列表快许多,但缺点在于无序。
接下来看看第2种方式:
2.直接对数组进行集合转化,然后再转回数组:
# 第二种去重方式def fast_way()return list(set(DUPLICATES))
耗时:
timeit fast_way()14.2 ms ± 1.73 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
平均耗时14毫秒,这种去重方式是最快的,但正如前面所说,集合是无序的,将数组转为集合后再转为列表,就失去了原有列表的顺序。
如果现在有保留原数组顺序的需要,那么这个方式是不可取的,怎么办呢?
3.保留原有数组顺序的去重
使用dict.fromkeys()函数,可以保留原有数组的顺序并去重:
def save_order():return list(dict.fromkeys(DUPLICATES))
当然,它会比单纯用集合进行去重的方式耗时稍微久一点:
timeit save_order()39.5 ms ± 8.66 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
平均耗时在39.5毫秒,我认为这是可以接受的耗时,毕竟保留了原数组的顺序。
但是,dict.fromkeys()仅在Python3.6及以上才支持。
如果你是Python3.6以下的版本,那么可能要考虑第四种方式了。
4. Python3.6以下的列表保留顺序去重
在Python3.6以下,其实也存在fromkeys函数,只不过它由collections提供:
from collections import OrderedDictdef save_order_below_py36():return list(OrderedDict.fromkeys(DUPLICATES))
耗时:
timeit save_order_below_py36()71.8 ms ± 16.9 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
平均耗时在72毫秒左右,比 Python3.6 的内置dict.fromkeys()慢一些,因为OrderedDict是用纯Python实现的。
以上就是对于python中4种列表去重方式的分析对比。欢迎在留言中分享你的观点。如果文章对你有帮助,欢迎转发/点赞/收藏~
作者:Ckend
_往期文章推荐_
