幂等 —— 让函数再次纯洁
幂等 —— 让函数再次纯洁
纯洁地做人,是一种美德。写纯函数,是程序员的美德。
纯函数
纯函数的美德就是,对于同样的输入,总是给予相同的输出,不改变系统的状态,不产生非预期的行为。非纯函数会导致各种意想不到的后果,并且很难排查原因。曾经遇到过一个奇葩的偶现问题,就是由于非纯函数导致的,后面花费了很长时间才定位到问题,详见:《做纯洁的人,写纯洁的代码》一文中的血淋淋的例子。
虽然总是呼吁大家写纯函数,但现实总是会接触到不纯的函数代码。上文中提到的例子,最后的修复办法也是改写了不纯的部分代码,让原来的不纯的函数成为一个纯函数。那个问题虽然难以重现和排查,但好在修改起来的代码量非常小,改写是容易的。除这种情况之外,本文又提供了一个案例,不仅排查困难,而且改写也麻烦。在这种情况下,又提供了另一种方式,只需要在不纯的函数头部添加一个幂等修饰符,就让它再次纯洁起来,这样完全可以不用改写。
一般我们说幂等,是从系统外部视角,针对的是用户做的某些操作,映射为后端服务中的某些 API。比如我们常说某某接口是幂等的,特别是 GET 请求的接口,只要输入参数一样,返回结果永远一样。本文实现的幂等修饰符,是方法级别的,粒度更细。当然,如果这个方法本来就是纯函数,自然不需要这个幂等修饰符了。如果某个方法有副作用,它就派上了用场,可以在不改变方法实现的前提下,让它的行为和纯函数一样,完全不需要了解函数到底做了啥。
本文将从实际问题引入,并以 TDD (非教条主义的)的开发方式,以及渐进增强的思想,逐步实现这个“幂等修饰符”。具体编程语言是该实际项目用到的 TypeScript。
非纯函数惹的祸
但是,如果维护一个屎山项目时,你不要期待迎接你的全是纯函数。我最近遇到一个情况,对于系统中的消息通知呀,有时候有用户反映,一模一样的通知,会收到两条甚至更多条。
简要分析和修复想法
我看了一下代码,发送消息是由一个长长的函数进行处理的,而这个函数有很多触发路径,比如接口触发、定时触发、消息队列触发等等,所以要从源头找出原因并不容易。
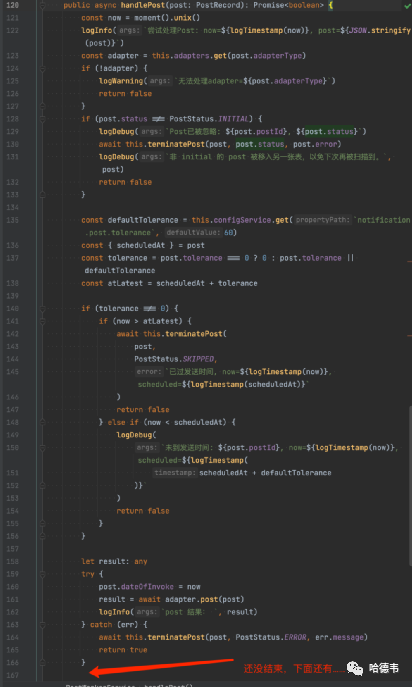
可以看到,它的输入参数是一个名为 post 的 PostRecord 对象,好在它有一个的 postId 键值,同一个消息推送通知,拥有一个唯一的 postId 键值:
export class PostRecord {...@Expose()postId: string...}
它的问题在于,对于同一个 postId 的消息推送通知对象,被不同的调用路径分别处理了多次,所以很自然的想法是,使用 postId 作为缓存键,将发送结果(布尔值)作为缓存值,将第一次执行的结果保存下来,后面的执行直接短路返回第一次执行的结果值。而且,通过修饰符来添加这个功能,似乎是最优雅的,因为对原有代码没有任何修改,只在方法头部增加一行而已:
+ ()public async handlePost(post: PostRecord): Promise{...
版本一:一个幼稚的实现
只考虑一个服务实例的情况,也就是一个进程。那么只需要使用一个内存变量来做这个缓存存储就行了。
先写测试
有了这个想法,为了文档、以及保证后面的扩展过程顺利,先写测试来构建安全屏障。尽管测试也是一个一个实现的,但为了行文不啰嗦,这里直接贴出主要测试用例代码:
import { idempotent } from '@/utils/idempotent'let count = 0class TestingClass {()testMethod() {console.log('adding count = ', count)return count++}}describe('idempotent', () => {it('a function without idempotent annotation would be called multiple times', async () => {let c = 0const testFunction = jest.fn().mockImplementation(() => c++)testFunction()testFunction()expect(testFunction).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(2)expect(c).toEqual(2)})it('a function with idempotent annotation would only be called once', async () => {const sut = new TestingClass()sut.testMethod()sut.testMethod()expect(count).toEqual(1)})})
其实,主要的测试意图就是,多次调用一个方法,如果该方法没有幂等修饰符,那么该方法带来的影响是多次执行;而如果这个方法有幂等修饰符呢,其效果是只有第一次是真正执行了,后续的执行被短路了。于是写了这样的一个幼稚实现版本:
实现
const cache = {}export function idempotent() {console.log('making ', ' idempotent')return function (target, propertyKey, descriptor) {console.log('idempotent called: ', target, propertyKey, descriptor)console.log('target.propertyKey = ', target[propertyKey].toString())const originalMethod = descriptor.valuedescriptor.value = () => {console.log('cache = ', cache)if (typeof cache[propertyKey] === 'undefined') {cache[propertyKey] = originalMethod()}return cache[propertyKey]}console.log('target.propertyKey now = ', target[propertyKey].toString())}}
提交代码。
增强版本
然后再回头审视代码,这个缓存键用了方法名,但没有类信息,会导致不同类的同一方法名,出现混淆情况。我们将类的信息也编码到缓存键里去:
const cache = {}export function idempotent() {- console.log('making ', ' idempotent')return function (target, propertyKey, descriptor) {- console.log('idempotent called: ', target, propertyKey, descriptor)- console.log('target.propertyKey = ', target[propertyKey].toString())-+ const cacheKey = `${target.constructor}.${propertyKey}`const originalMethod = descriptor.valuedescriptor.value = () => {- console.log('cache = ', cache)- if (typeof cache[propertyKey] === 'undefined') {- cache[propertyKey] = originalMethod()+ if (typeof cache[cacheKey] === 'undefined') {+ cache[cacheKey] = originalMethod()}- return cache[propertyKey]+ return cache[cacheKey]}-- console.log('target.propertyKey now = ', target[propertyKey].toString())}}
测试通过,提交代码。
再次审视,我们需要将对象的信息编码进入缓存键中,不然,同一个类下的不同对象之间也会出现混淆,这是一个后面的优化点。
继续增强——支持参数
以上的实现版本,幂等装饰器是一个不带参数的函数。这次再增强一下,允许传入一个函数作为幂等装饰器的参数,该函数接收装饰目标方法的参数为参数,并返回一个键值,成为缓存键的一部分。整个过程就不啰嗦了,为了测试这些场景,新的测试文件内容如下:
import { idempotent } from '@/utils/idempotent/idempotent'describe('idempotent', () => {describe('idempotent without key', () => {let count = 0class TestingClass {()async testMethod() {return count++}}it('a function without idempotent annotation would be called multiple times', async () => {let c = 0const testFunction = jest.fn().mockImplementation(() => c++)testFunction()testFunction()expect(testFunction).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(2)expect(c).toEqual(2)})it('a function with idempotent annotation would only be called once', async () => {const sut = new TestingClass()await Promise.all([sut.testMethod(), sut.testMethod()])expect(count).toEqual(1)})})describe('idempotent with key', () => {class TestingClass {((obj) => obj.id)testMethod(obj: { id: string; count: number }) {obj.count++return obj.count}}it('calls testMethod multiple times, only the 1st one takes effect', async () => {const sut = new TestingClass()const obj1 = { id: '1', count: 0 }const obj2 = { id: '2', count: 0 }sut.testMethod(obj1)sut.testMethod(obj1)sut.testMethod(obj2)expect(obj1.count).toEqual(1)expect(obj2.count).toEqual(1)})})})
其实,主要的测试意图就是,多次调用一个方法,如果该方法没有幂等修饰符,那么该方法带来的影响是多次执行;而如果这个方法有幂等修饰符呢,其效果是只有第一次是真正执行了,后续的执行被短路了。然后,分别考虑这个方法接收参数与不接收参数的场景,不接收参数,该方法至多只会被执行一次;接收参数,对“同样的”参数至多只执行一次。但是这个“同样”的涵义,是在写修饰符时定义的。也就是说,这个修饰符自己也接受一个参数,用来定义这个“同样”。比如根据参数的某个唯一属性决定,或者自行实现一个哈希值进行比对,都可以。
满足这样的测试的装饰器实现如下:
import * as crypto from 'crypto'import { sleep } from '@/common'const inMemoryStorage = {executedMethods: {},returnValues: {},}export enum MethodStatus {pending = 0,done = 1,error = 2,}export interface IIdempotentStorage{get: (hash: string) => PromisesaveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted: (hash: string, valueEvaluator: () => Promise) => Promise}export class HashDuplicationError extends Error {}export class OriginalMethodError extends Error {constructor(readonly originalError: Error) {super()}}export class InMemoryIdempotentStorageimplements IIdempotentStorage{async saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted(hash: string, valueEvaluator: () => Promise) {if (inMemoryStorage.executedMethods[hash] === undefined) {inMemoryStorage.executedMethods[hash] = MethodStatus.pendingtry {inMemoryStorage.returnValues[hash] = await valueEvaluator()} catch (ex) {inMemoryStorage.executedMethods[hash] = MethodStatus.errorinMemoryStorage.returnValues[hash] = exthrow new OriginalMethodError(ex)}inMemoryStorage.executedMethods[hash] = MethodStatus.done}}async get(hash) {if (inMemoryStorage.executedMethods[hash] === MethodStatus.error) {throw new OriginalMethodError(inMemoryStorage.returnValues[hash])}if (inMemoryStorage.executedMethods[hash] !== MethodStatus.done) {await sleep(500)return await this.get(hash)}return inMemoryStorage.returnValues[hash]}}export function idempotent(hashFunc?, idempotentStorage: IIdempotentStorage= new InMemoryIdempotentStorage()) {return function (target, propertyKey, descriptor) {const cachePrefix = `${crypto.createHash('md5').update(target.constructor.toString()).digest('hex')}.${propertyKey}`const originalMethod = descriptor.valuedescriptor.value = async function (...args) {const hash = hashFunc ? hashFunc(...args) : ''const cacheKey = `${cachePrefix}:${hash}`const fallback = async () => await originalMethod.call(this, ...args)const idempotentOrFallback = async () =>await Promise.race([idempotentStorage.get(cacheKey),new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(reject, 30000)),]).catch(fallback)try {await idempotentStorage.saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted(cacheKey, fallback)} catch (ex) {// if it's duplicate error, wait for done and then getif (ex instanceof HashDuplicationError) {return await idempotentOrFallback()} else if (ex instanceof OriginalMethodError) {throw ex.originalError} else {console.error(ex)return await fallback()}}return await idempotentOrFallback()}}}
这中间跳跃比较大了,实际情况并不是一步到位的。有一个改动比较明显,即装饰器函数变复杂了。其中 descriptor.value 不再用箭头表达式,而是用了 function。这是为了利用 this,保证如果目标方法依赖类中的其他属性或者成员,在被装饰器改写后,仍然可以照常使用,而不会报 某某方法、成员、或者属性在 undefined 中不存在等之类的错误。
还可以看到,内存缓存不再是一个对象,而是包括了两个对象的对象。这是由于考虑到异步函数,存在方法正在执行但是返回结果还没有拿到的情况,所以增加了executedMethods做为了一个互斥锁。并且将装饰器的依赖,显式使用接口 IIdempotentStorage 说明,不再隐式依赖内存缓存。同时,使用 class 方式实现了使用内存缓存的幂等存储接口 IIdempotentStorage 。
这个接口设计上只有两个方法,即 saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted 和 get。get 显然就是用来获取缓存值的,并且保证获取到值,如果装饰目标函数正在运行,值还没有拿到,这个 get 不会返回,也不会返回空,而是会等待一段时间,再去获取,直到获取到值。若因为某种原因一直拿不到返回值,最终这个装饰目标方法会报超时错误,这个逻辑见装饰器的代码。
这个接口的另一方法,叫 saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted,会被装饰后的方法首先执行。这个方法名很长,正如这个名字暗示的,只会在第一次执行原方法时保存返回值到存储中。这个方法,在执行原方法时,需要先检查是不是已经有一个实例在执行中了,即需要先拿到一个互斥锁。所以会在 InMemoryIdempotentStorage看到对之前说的 executedMethods进行检查。由于是内存存储,通过这个锁来防止对原方法的重复调用是简单且有效的,在后面增加非内存存储时,就需要利用别的机制了,会更复杂一些。
版本二:支持多个服务实例
在版本一实现后,非常清楚这个方式解决问题的关键在于需要一个缓存存储。内存版本只能支持一个服务实例,要支持多个服务实例,我们必须找到一个外部存储,这个外部存储可以是 Redis、也可以是其他数据库。本文采用了 DynamoDb 作为缓存存储,因为该项目已经引用了 AWS 的 DynamoDb,并且没有使用 Redis,所以继续沿用不需要增加依赖。如果使用 Redis 的话,可以考虑使用 RedLock 这个库,它应该是利用了 Redis 的分布式锁功能。据说 DynamoDb 也有分布式锁方案,但是本文没有采用分布式锁,而且利用了数据库的唯一约束,完成了幂等功能,详见后面的叙述。
测试先行
既然决定了使用 DynamoDb,那么有个挑战就是如果在测试时,排除 DynamoDb 这个外部依赖。好在之前有文章《扫清 Cloud Native 开发时的 TDD 障碍》已经部分解决了这个挑战,即通过 Mockery 将 AWS SDK 中的方法用 jest.fn() 去模拟掉了,但是,本篇文章的需求,要使用更多的 AWS SDK 中的方法,所以需要在那篇文章的基础上,增加更多的模拟。
主要是,在实现接口的 saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted方法时,需要利用数据库的唯一约束,在多次写入同一键值时,能够让数据库报错。这里使用了 AWS DynamoDb 的 transactWriteItems方法,在测试中,需要将它模拟掉:
export const mockDynamoDB = {+ transactWriteItems: jest.fn().mockImplementation((params: DynamoDB.Types.TransactWriteItemsInput) => {+ return {+ promise: () => {+ const hash = params.TransactItems[0].Put?.Item['hash'].S++ if (!hash) {+ return Promise.reject('hash empty!')+ }++ if (!db[hash]) {+ db[hash] = params.TransactItems[0].Put?.Item+ return Promise.resolve()+ } else {+ return Promise.reject('duplicated!')+ }+ },+ }+ }),+ describeTable: jest.fn().mockImplementation(({ TableName }) => {+ return {+ promise: () => {+ return Promise.resolve({ TableName })+ },+ }+ }),createTable: jest.fn().mockImplementation(() => {return {
打通了这个自动化测试障碍,就可以写测试用例了。主要的测试目的,就是验证当我们实现了基于 DynamoDb 的幂等存储后,如果尝试多次调用 saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted方法,只有第一次的调用能够成功,而重复的调用应该抛错,并且 get只会取到第一次存储的值。
import { mockAwsSdk } from '../../../test/mocks/aws'jest.mock('aws-sdk', () => mockAwsSdk)import { DynamodbIdempotentStorage } from '@/utils/idempotent/dynamodb.idempotent.storage'import { AWSAdapterService } from '@/common/adapters/aws'import { HashDuplicationError } from '@/utils/idempotent/idempotent'describe('dynamodb.idempotent.storage', () => {it('throws HashDuplicationError when saving duplicate hash record', async () => {const dynamodbStorage = new DynamodbIdempotentStorage(new AWSAdapterService())await dynamodbStorage.saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted('1234', async () => {return 'hello'})await expect(async () => {await dynamodbStorage.saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted('1234', async () => {return 'world2'})}).rejects.toThrow(HashDuplicationError)const res = await dynamodbStorage.get('1234')expect(res).toStrictEqual('hello')})})
基于 DynamoDb 的幂等存储
也不啰嗦,最后的实现大致是这样的:
import {HashDuplicationError,IIdempotentStorage,MethodStatus,OriginalMethodError,} from '@/utils/idempotent/idempotent'import { BaseDynamoService } from '@/common/base'import { Expose, plainToClass } from 'class-transformer'import { DynamoDB } from 'aws-sdk'import { sleep } from '@/common'export class IdempotentCache {()hash: string()status: MethodStatus()returnValue: string()ttl: number}const getTtl = () => Math.floor(new Date().getTime() / 1000 + 3600 * 24)export class DynamodbIdempotentStorageextends BaseDynamoServiceimplements IIdempotentStorage{async get(hash: string): Promise{const record = await this.getItem({TableName: this.table,Key: {hash: { S: hash },},})if (record && record.status.toString() === MethodStatus.error.toString()) {throw new OriginalMethodError(new Error(record.returnValue))}if (!record || record.status.toString() !== MethodStatus.done.toString()) {console.log('record of ', hash, ' = ', record)await sleep(500)return await this.get(hash)}return record?.returnValue ? JSON.parse(record?.returnValue) : undefined}async saveReturnValuesIfNotExecuted(hash: string, valueEvaluator: () => Promise): Promise{await this.ensureTable(this.table)try {await this.transactionalWriteItems({TransactItems: [{Put: {TableName: this.table,ConditionExpression: 'attribute_not_exists(#hsh)',ExpressionAttributeNames: { '#hsh': 'hash' },Item: this.toAttributeMap({hash,status: MethodStatus.pending,returnValue: '',ttl: getTtl(),}),},},],})} catch (ex) {console.error(ex)throw new HashDuplicationError(ex.message)}let returnValuetry {returnValue = await valueEvaluator()} catch (ex) {const item = this.toAttributeMap({hash,status: MethodStatus.error,returnValue: ex.message,ttl: getTtl(),})await this.putItem({TableName: this.table,Item: item,})throw new OriginalMethodError(ex)}const item = this.toAttributeMap({hash,status: MethodStatus.done,returnValue: JSON.stringify(returnValue),ttl: getTtl(),})await this.putItem({TableName: this.table,Item: item,})}protected getTableConfig(): Partial{return {TableName: this.table,AttributeDefinitions: [{AttributeName: 'hash',AttributeType: 'S',},],KeySchema: [{AttributeName: 'hash',KeyType: 'HASH',},],}}protected toAttributeMap(record: IdempotentCache): DynamoDB.AttributeMap {return {hash: this.toS(record.hash),status: this.toS(record.status),returnValue: this.toS(record.returnValue),ttl: this.toN(record.ttl),}}protected toInstance(item: DynamoDB.AttributeMap): IdempotentCache {return plainToClass(IdempotentCache, {hash: this.toValue(item.hash),status: this.toValue(item.status),returnValue: this.toValue(item.returnValue),ttl: this.toValue(item.ttl),})}protected getTTLConfig(): Partial| null {return {TimeToLiveSpecification: {Enabled: true,AttributeName: 'ttl',},}}}
这个实现,依赖了一个 BaseDynamoService,关于它的更多信息,见之前的《强行在 TypeScript 里应用 C# 的 partial class》,其实就是对 Aws Sdk 中的 DynamoDb 做了一些封装。
另外,利用了 DynamoDb 的 ttl 机制,只缓存一天的数据。
关于前面和这里反复用到的 sleep 函数,相信你分分钟就能写一个吧,不做赘述。
测试通过,提交代码。
在真实的 AWS 环境里测试
尽管测试愉快地通过了,但那都是基于我们模拟的环境。如果放在真实的 AWS 环境,它真的会如期工作吗?真的会!
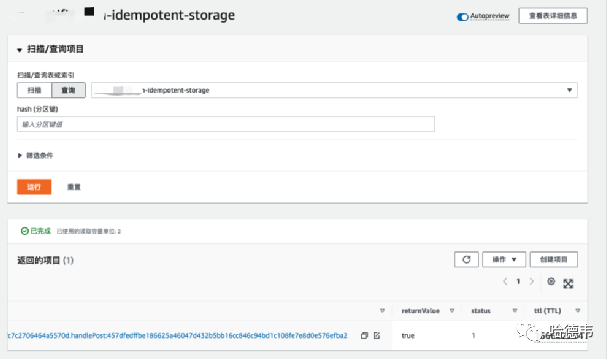
这里分享一下从本地连接真实的 AWS 环境进行测试的技巧。首先,需要安装 aws 命令行,登录之后,你可以 cat ~/.aws/config 看到一些关键信息,如:
[default]aws_access_key_id = xxxxaws_secret_access_key = yyyaws_session_token = zzzoutput = jsonregion = cn-northwest-1
要在跑测试时,通过以上信息连接到真实的 AWS 环境,需要将环境变量 AWS_SDK_LOAD_CONFIGx0;设置为 1,于是要么:
AWS_SDK_LOAD_CONFIG=1 yarn test要么,在测试文件顶部加入:
process.env['AWS_SDK_LOAD_CONFIG'] = '1'并且删除之前的对 mock 的执行:
+ process.env['AWS_SDK_LOAD_CONFIG'] = '1'- import { mockAwsSdk } from '../../../test/mocks/aws'- jest.mock('aws-sdk', () => mockAwsSdk)
ADFS?
如果你的 AWS 登录采用了 adfs,那么推荐使用 https://github.com/Jeff-Tian/aws-adfs-auth ,让你可以在命令行里直接登录 AWS。详见使用教程见其 README。
使用基于 DynamoDb 的幂等存储
到了这一步,我们已经走了很远。现在回头来解决最初的问题。在简要分析与修复想法中,我们希望只通过添加一个幂等修饰符,不改其他代码,就修复掉重复发消息的问题。于是最终的代码改动如下:
+ ((post) => post.postId, new DynamodbIdempotentStorage())public async handlePost(post: PostRecord): Promise{
上线后,再也没有出现用户收到重复消息的问题了。
思考与总结
为什么没有使用 memoize 模式?
memoize 是我很喜欢的一个模式,它不仅也让不纯的函数变得纯洁,而且实现起来非常简洁。在之前的文章中我一再提到它:
但是这次没有采用,因为它也是利用内存做为缓存,更适合只有一个实例的场景,比如用在前端就很好。但是基于要用到数据库的原因,就没有采用它。
发布 npm 包
如果后面再发现其它项目中也需要用它,或者本文点赞数过千,那说明这个装饰器很有复用价值,到那时再发布成一个 npm 包。
