工作中可能会使用到的数据结构和算法
背景
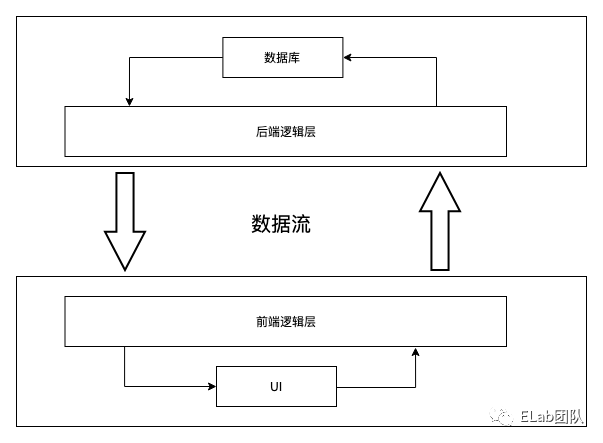
我们日常的开发工作避免不了和数据打交道。展示数据时,接口返回的数据结构可能没办法直接拿来使用,需要做一层转换;保存数据时,通过表单拿到的数据结构和接口定义的数据结构也可能不一致,需要做一层转换;还有一些业务场景本身的需要,需要对数据的逻辑校验等。因此避免不了会使用到一些常用的数据结构和算法。本文主要是讨论在前端开发工作中,可能会使用到的数据结构和算法。
数据结构
栈
栈是一种特殊的线性表。它的特点是,只能在表的一端操作。可以操作的端称为栈顶,不可以操作的另一端称为栈底。栈的特性:先进后出。
原理
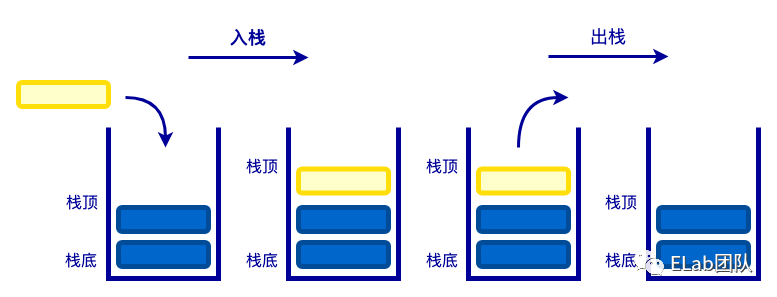
生活中的例子:蒸馒头的笼屉、羽毛球筒。
实现
我们可以使用 JS 来模拟栈的功能。从数据存储的方式来看,可以使用数组存储数据,也可以使用链表存储数据。因为数组是最简单的方式,所以这里是用数组的方式来实现栈。
栈的操作包括入栈、出栈、清空、获取栈顶元素、获取栈的大小等。
class Stack {
constructor() {
// 存储数据
this.items = [];
}
push(item) {
// 入栈
this.items.push(item);
}
pop() {
// 出栈
return this.items.pop();
}
top() {
// 获取栈顶元素
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
clear() {
// 清空栈
this.items = [];
}
size() {
// 获取栈的大小
return this.items.length;
}
isEmpty() {
// 判断栈是否为空
return this.items.length === 0;
}
}
应用
判断括号是否匹配
方法一思路分析:
首先从头到尾遍历整个字符串; 当遇到字符"("则入栈,遇到字符")"则出栈; 出栈时,如果栈已经为空,则返回 false; 当字符串遍历完毕以后,判断栈是否为空。
方法二思路分析:
声明变量 num 为 0,并从头到尾遍历整个字符串; 当遇到字符"("则 num 加 1,遇到字符")"num 减 1; 在遍历的过程中,当 num 减 1 时,num 的值已经为 0 则返回 false; 当字符串遍历完毕以后,判断 num 是否为 0。
// 方式一:栈
function isPairing(str = '') {
const stack = new Stack();
for(let i of str) {
if (i === '(') {
stack.push(i);
} else if (i === ')') {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
return stack.size() === 0;
}
// 方式二:计数
function isPairing(str = '') {
let num = 0;
for(let i of str) {
if (i === '(') {
num++;
} else if (i === ')') {
if (num === 0) {
return false;
} else {
num--;
}
}
}
return num === 0;
}
判断 HTML 标签是否匹配
思路分析:
声明变量 stack、nodes;并从头遍历 HTML 字符串,查找字符"<"的位置;
如果字符"<"的位置等于 0:
则继续尝试匹配 HTML 结束标签,匹配成功并且与栈顶的标签名称一致,则弹出栈顶;否则报错; 匹配 HTML 结束标签失败以后,则尝试匹配开始标签的起始部分,然后循环匹配标签属性对,最后匹配开始标签的结束部分。匹配完成以后,将匹配到的标签压入栈顶;并构建 node 节点数; 如果字符"<"的位置大于 0:
则 html.slice(0, pos),创建文本节点。
function parseHtml(html = '') {
const startIndex = 0;
const endIndex = 0;
// 匹配标签<div>、<br/>等标签的开始部分"<div、<br"
const startTagOpen = /^<([a-zA-Z\d]+)/;
// 匹配标签<div>、<br/>等标签的闭合部分">、/>"
const startTagClose = /^\s*(\/?)>/;
// 匹配属性
const attribute = /^\s*([\w-]+)(?:="([^"]*)")?\s*/;
// 匹配闭合标签,例如</div>、</p>
const endTag = /^<\/([a-zA-Z\d]+)>/;
const stack = [];
const nodes = [];
while(html) {
// 查找<的起始位置
const index = html.indexOf('<');
if (index === 0) {
// 先匹配整体结束标签,例如</div>、</p>
let endTagMatch = html.match(endTag);
if (endTagMatch) {
if (stack[stack.length - 1]) {
if (stack[stack.length - 1].tag === endTagMatch[1]) {
// 出栈
stack.pop();
advanced(endTagMatch[0].length);
continue;
} else {
throw new Error(`起始标签和结束标签不匹配: 起始标签(${stack[stack.length - 1].tag}),结束标签(${endTagMatch[0]})`);
}
} else {
throw new Error(`${endTagMatch[0]}没有起始标签`);
}
}
// 然后匹配起始标签的开始部分,例如<div>的<div、<p>的<p、<br/>的<br
let startTagOpenMatch = html.match(startTagOpen);
if (startTagOpenMatch) {
const node = {
nodeType: 1,
tag: startTagOpenMatch[1],
attrs: [],
children: [],
};
advanced(startTagOpenMatch[0].length);
let end, attr;
// 匹配标签属性列表
while(!(end = html.match(startTagClose)) && (attr = html.match(attribute))) {
advanced(attr[0].length);
node.attrs.push({
name: attr[1],
value: attr[2],
});
}
// 匹配起始标签的结束部分
if (end) {
if (stack.length === 0) {
nodes.push(node);
} else {
stack[stack.length - 1].children.push(node);
}
// 自闭和标签不加入栈中
if (end[1] !== '/') {
stack.push(node);
}
advanced(end[0].length);
}
}
} else {
// 文本
const node = {
nodeType: 3,
textContent: html.slice(0, index)
};
if (stack.length === 0) {
nodes.push(node);
} else {
stack[stack.length - 1].children.push(node);
}
advanced(node.textContent.length);
}
}
function advanced(n) {
html = html.substring(n);
}
return nodes;
}
parseHtml('<div id="test" class="a b"></div>');
parseHtml('<div id="test" class="a b">Hello World</div>');
parseHtml('开始<div id="test" class="a b">Hello World</div>');
parseHtml('<div id="test" class="a b"><br class="br" />Hello World</div>');
parseHtml('</div>');
parseHtml('<div></p>');
版本号比较大小
思路分析:
版本号 v1、v2 按照符号"."分割成数组,从左右依次进行大小比较; v1 大于 v2 返回 1,v2 小于 v2 返回-1,v1 等于 v2 返回 0。
/*
比较版本号大小
v1:第一个版本号
v2:第二个版本号
如果版本号相等,返回 0, * 如果第一个版本号低于第二个,返回 -1,否则返回 1.
*/
function compareVersion(v1, v2) {
if (!v1 && !v2) return 0;
if (!v1) return -1;
if (!v2) return 1;
const v1Stack = v1.split('.');
const v2Stack = v2.split('.');
const maxLen = Math.max(v1Stack.length, v2Stack.length);
for(let i = 0; i < maxLen; i++) {
// 必须转整,否则按照字符顺序比较大小
const prevVal = ~~v1Stack[i];
const currVal = ~~v2Stack[i];
if (prevVal > currVal) {
return 1;
}
if (prevVal < currVal) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
console.log(compareVersion("2.2.1", "2.2.01")); // 0
console.log(compareVersion("2.2.1", "2.2.0")); // 1
console.log(compareVersion("2.2.1", "2.1.9")); // 1
console.log(compareVersion("2.2", "2.1.1")); // 1
console.log(compareVersion("2.2", "2.2.1")); // -1
console.log(compareVersion("2.2.3.4.5.6", "2.2.2.4.5.12")); // 1
console.log(compareVersion("2.2.3.4.5.6", "2.2.3.4.5.12")); // -1
用途
Vue 模板编译将模板字符串转换成 AST。 自动更新最新版本的 NPM 包。 函数执行上下文栈。
队列
队列也是一种特殊的线性表,它的特点是,只能在表的一端进行删除操作,而在表的另一点进行插入操作。可以进行删除操作的端称为队首,而可以进行插入操作的端称为队尾。删除一个元素称为出队,插入一个元素称为入队。和栈一样,队列也是一种操作受限制的线性表。队列的特性:先进先出 (FIFO,First-In-First-Out)。
原理
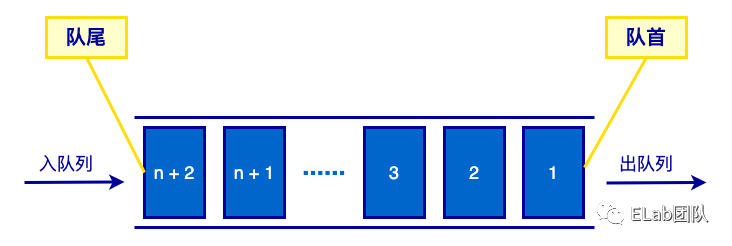
生活中的例子:排队买东西。
实现
我们也可以使用 JS 来模拟队列的功能。从数据存储的方式来看,可以使用数组存储数据,也可以使用链表存储数据。因为数组是最简单的方式,所以这里是用数组的方式来实现队列。
队列的操作包括入队、出队、清空队列、获取队头元素、获取队列的长度等。
class Queue {
constructor() {
// 存储数据
this.items = [];
}
enqueue(item) {
// 入队
this.items.push(item);
}
dequeue() {
// 出队
return this.items.shift();
}
head() {
// 获取队首的元素
return this.items[0];
}
tail() {
// 获取队尾的元素
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
clear() {
// 清空队列
this.items = [];
}
size() {
// 获取队列的长度
return this.items.length;
}
isEmpty() {
// 判断队列是否为空
return this.items.length === 0;
}
}
应用
约瑟夫环问题
有一个数组存放了 100 个数据 0-99,要求每隔两个数删除一个数,到末尾时再循环至开头继续进行,求最后一个被删除的数字。
思路分析
创建队列,将 0 到 99 的数字入队; 循环队列,依次出列队列中的数字,对当前出队的数字进行计数 index + 1; 判断当前出列的 index % 3 是否等于 0,如果不等于 0 则入队; 直到队列的长度为 1,退出循环,返回队列中的数字。
function ring(arr) {
const queue = new Queue();
arr.forEach(v => queue.enqueue(v));
let index = 0;
while(queue.size() > 1) {
const item = queue.dequeue();
if (++index % 3 !== 0) {
queue.enqueue(item);
}
}
return queue.head();
}
斐波那契数列
斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),又称黄金分割数列,因数学家莱昂纳多·斐波那契(Leonardoda Fibonacci)以兔子繁殖为例子而引入,故又称为“兔子数列”,指的是这样一个数列:0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34、……在数学上,斐波那契数列以如下被以递推的方法定义:F(0)=0,F(1)=1, F(n)=F(n - 1)+F(n - 2)(n ≥ 2,n ∈ N*)。
function fiboSequence(num) {
if (num < 2) return num;
const queue = [];
queue.push(0);
queue.push(1);
for(let i = 2; i < num; i++) {
const len = queue.length;
queue.push(queue[len - 2] + queue[len - 1]);
}
return queue;
}
打印杨辉三角

思路分析:
通过观察发现,三角中的每一行数据都依赖于上一行的数据; 我们首先创建队列 queue,用于存储每一行的数据,供下一行数据使用; 然后初始化第一行的数据 1 入队,这里需要两个 for 循环嵌套,外层的 for 循环决定最终打印的总行数,内层的 for 循环生成每行的数据; 在生成当前行的数据时,将队列中的数据源依次出队,然后将新生成的数据入队;并记录当前出队的数据,供生成新数据使用。
function printYangHui(num) {
const queue = [];
// 存储第一行数据
queue.push(1);
for(let i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
let rowArr = [];
// 填充空格
for(let j = 0; j < Math.floor((num - i) / 2); j++) {
rowArr.push('');
}
let prev = 0;
for(let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
const num = queue.shift();
queue.push(prev + num);
rowArr.push(num);
prev = num;
}
queue.push(1);
console.log(rowArr.join(' '));
}
}
printYangHui(10);
用途
实现洋葱模型
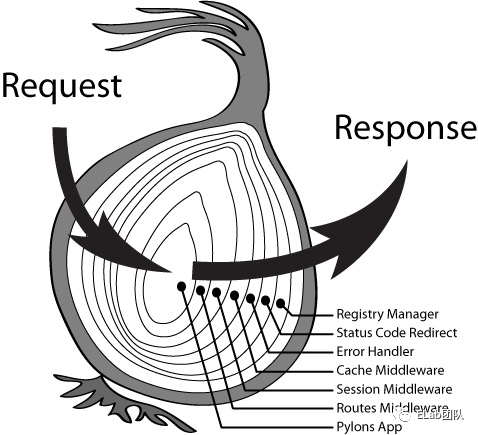
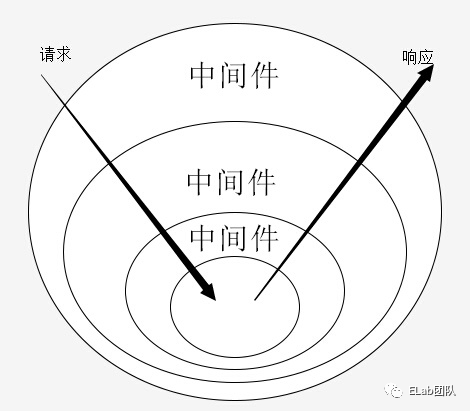
完善代码,实现输出 1、2、3。
function createApp(){
return {
use(fn){},
run(){},
}
}
const app = createApp();
app.use((next)=>{
setTimeout(function(){
next();
})
console.log(new Date() ,'1');
})
app.use((next)=>{
console.log(new Date() ,'2');
next();
})
app.use((next)=>{
console.log(new Date() ,'3');
next();
})
app.run();
消息队列
链表
由若干个结点链结成一个链表,称之为链式存储结构。
链表和数组的区别
链表和数组都可以存储多个数据,那么链表和数组有什么区别呢?
数组需要一块连续的内存空间来存储数据,对内存的要求比较高。而链表却相反,它并不需要一块连续的内存空间。链表是通过指针将一组零散的内存块串联在一起。
相比数组,链表是一种稍微复杂一点的数据结构。两者没有好坏之分,各有各的优缺点。
由于内存存储特性,数组可以实现快速的查找元素,但是在插入和删除时就需要移动大量的元素。原因就在于相邻元素在内存中的位置也是紧挨着的,中间没有空隙,因此就无法快速添加元素。而当删除后,内存空间中就会留出空隙,自然需要弥补。
分类
单向链表
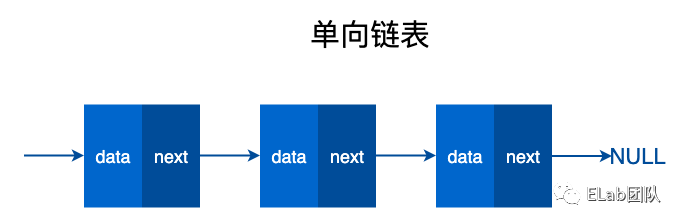
双向链表
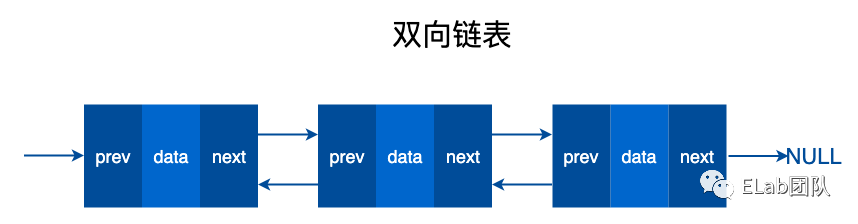
单向循环链表
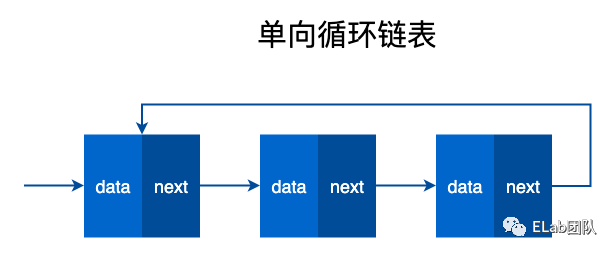
双向循环链表
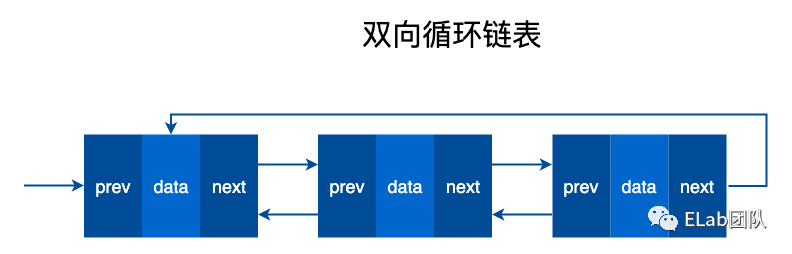
实现
const Node = function (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
const node1 = new Node(1);
const node2 = new Node(2);
const node3 = new Node(3);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
应用
环形链表
给定一个链表,如何判断链表中是否有环?
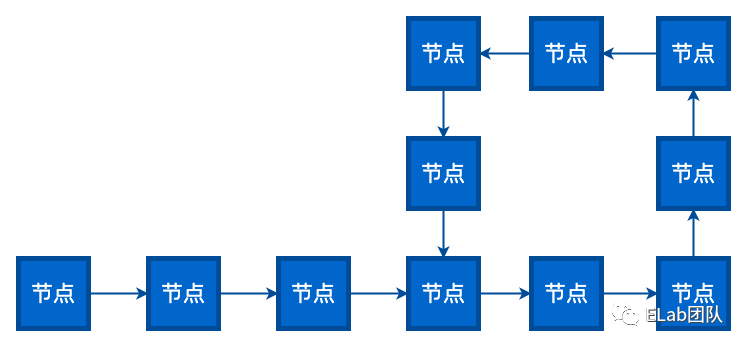
思路分析:
首先创建两个指针 1 和 2,同时指向这个链表的头节点。然后开始一个大循环,在循环体中,让指针 1 每次向下移动一个节点,让指针 2 每次向下移动两个节点,然后比较两个指针指向的节点是否相同。如果相同,则判断出链表有环,如果不同,则继续下一次循环。 例如链表 A->B->C->D->B->C->D,两个指针最初都指向节点 A,进入第一轮循环,指针 1 移动到了节点 B,指针 2 移动到了 C。第二轮循环,指针 1 移动到了节点 C,指针 2 移动到了节点 B。第三轮循环,指针 1 移动到了节点 D,指针 2 移动到了节点 D,此时两指针指向同一节点,判断出链表有环。 假设从链表头节点到入环点的距离是 D,链表的环长是 S。那么循环会进行 S 次,可以简单理解为 O(N)。除了两个指针以外,没有使用任何额外存储空间,所以空间复杂度是 O(1)。
const Node = function (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
const nodeA = new Node('A');
const nodeB = new Node('B');
const nodeC = new Node('C');
const nodeD = new Node('D');
const nodeE = new Node('E');
nodeA.next = nodeB;
nodeB.next = nodeC;
nodeC.next = nodeD;
nodeD.next = nodeE;
nodeE.next = nodeC;
function isCircularLinkedList(head) {
if (head === null || head.next === null) {
return false;
}
let point1 = head;
let point2 = head;
do {
point1 = point1.next;
point2 = point2.next && point2.next.next;
} while(point1 && point2 && point1 !== point2);
if (point1 === point2) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
console.log(isCircularLinkedList(nodeA));
相交链表
判断两个单链表是否相交并求出相交的第一结点。
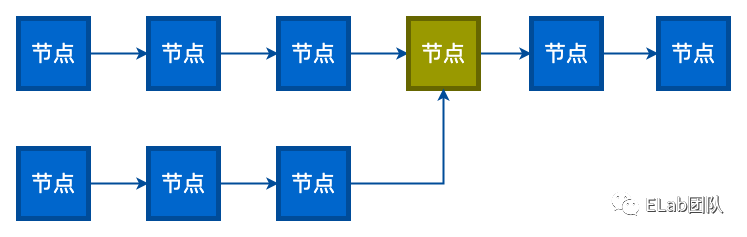
思路分析:
两个没有环的链表如果是相交于某一结点,如上图所示,这个结点后面都是共有的。所以如果两个链表相交,那么两个链表的尾结点的地址也是一样的。程序实现时分别遍历两个单链表,直到尾结点。判断尾结点地址是否相等即可。时间复杂度为 O(L1+L2)。 如何找到第一个相交结点?判断是否相交的时候,记录下两个链表的长度,算出长度差 len,接着先让较长的链表遍历 len 个长度,然后两个链表同时遍历,判断是否相等,如果相等,就是第一个相交的结点。
function intersectNode(head1, head2) {
if (head1 && head2) {
// 计算链表的长度
let len1 = 0, p = head1;
let len2 = 0, q = head2;
while(p.next) {
len1++;
p = p.next;
}
while(q.next) {
len2++;
q = q.next;
}
if (p === q) {
// p指向短链,q指向长链
let len = 0;
if (len1 > len2) {
len = len1 - len2;
p = head2;
q = head1;
} else {
len = len2 - len1;
p = head1;
q = head2;
}
while(len > 0) {
len--;
q = q.next;
}
while(p && q && p !== q) {
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
const Node = function (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
const nodeA = new Node('A');
const nodeB = new Node('B');
const nodeC = new Node('C');
const node1 = new Node('1');
const node2 = new Node('2');
const node3 = new Node('3');
const nodeD4 = new Node('D4');
const nodeE5 = new Node('E5');
nodeA.next = nodeB;
nodeB.next = nodeC;
nodeC.next = nodeD4;
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = nodeD4;
nodeD4.next = nodeE5;
console.log(intersectNode(nodeA, node1));
回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
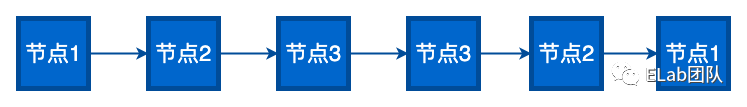
思路分析:
从头遍历链表,同时正向和反向拼接每个链表的数据,最后比对正向和反向得到的字符串是否相等。如果相等则是回文链表;否则不是。
const Node = function (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
const node1 = new Node('A');
const node2 = new Node('B');
const node3 = new Node('C');
const node4 = new Node('C');
const node5 = new Node('B');
const node6 = new Node('A');
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
node5.next = node6;
const isPalindrome = head => {
let a = '', b = '';
while(head !== null) {
a = a + head.data;
b = head.data + b;
head = head.next;
}
return a === b;
}
console.log(isPalindrome(node1));
用途
原型链 作用域链
树
树是一种数据结构,它是由 n(n>=1)个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把它叫做“树”是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。
分类
无序树:树中任意节点的子结点之间没有顺序关系,这种树称为无序树,也称为自由树。 有序树:树中任意节点的子结点之间有顺序关系,这种树称为有序树。 二叉树:每个节点最多含有两个子树的树称为二叉树。 满二叉树:叶节点除外的所有节点均含有两个子树的树被称为满二叉树。 完全二叉树:除最后一层外,所有层都是满节点,且最后一层缺右边连续节点的二叉树称为完全二叉树(堆就是一个完全二叉树)。 哈夫曼树(最优二叉树):带权路径最短的二叉树称为哈夫曼树或最优二叉树。
实现
// 二叉树的实现
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
const nodeA = new Node('A');
const nodeB = new Node('B');
const nodeC = new Node('C');
const nodeD = new Node('D');
const nodeE = new Node('E');
const nodeF = new Node('F');
const nodeG = new Node('G');
nodeA.left = nodeB;
nodeA.right = nodeC;
nodeB.left = nodeD;
nodeB.right = nodeE;
nodeC.left = nodeF;
nodeC.right = nodeG;
我们日常工作中接触到最多的是多叉树。
遍历
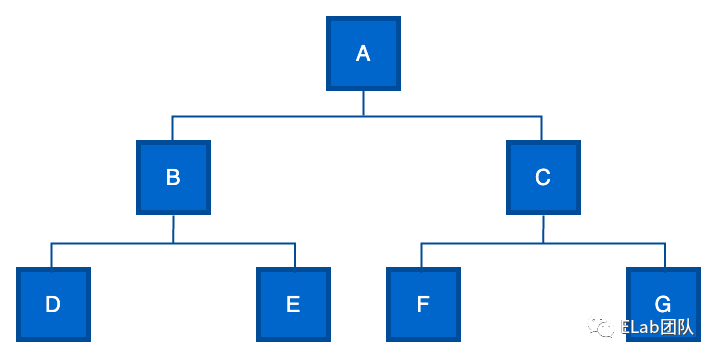
深度优先遍历
先序遍历
先序遍历(又称先根遍历)为 ABDECFG(根-左-右)。
中序遍历
中序遍历(又称中根遍历)为 DBEAFCG(左-根-右)(仅二叉树有中序遍历)。
后序遍历
后序遍历(又称后根遍历)为 DEBFGCA(左-右-根)。
广度优先遍历
层序遍历
层序遍历为 ABCDEFG。
用途
树的扁平化(展示 OCR 识别结果) 扁平化数组转换成树(标签树)
图
图(Graph)结构是一种非线性的数据结构,图在实际生活中有很多例子,比如交通运输网,地铁网络,等等都可以抽象成图结构。图结构比树结构复杂的非线性结构。
图是由若干个顶点和边组成。
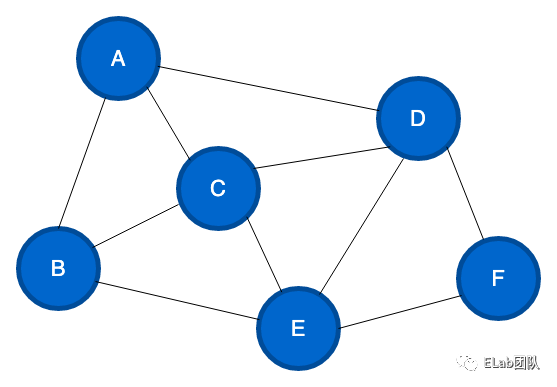
分类
无向图
如果一个图结构中,所有的边都没有方向性,那么这种图便称为无向图。
有向图
一个图结构中,边是有方向性的,那么这种图就称为有向图。
加权图
如果给边加上一个值表示权重,这种图就是加权图。
连通图
如果图中任意两个节点都能找到路径可以将它们进行连接,则称该图为连通图。
表示
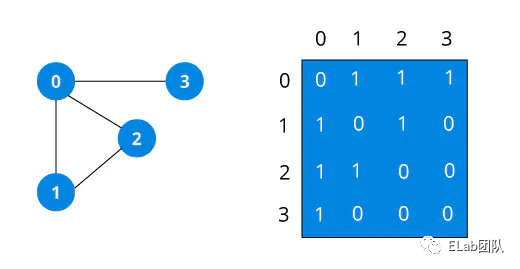
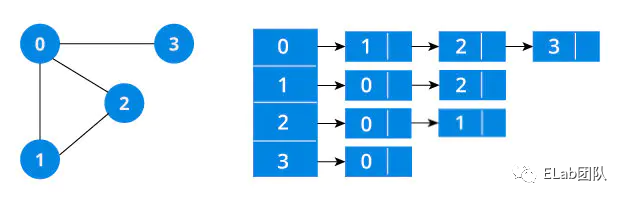
图有两种表示方法:邻接矩阵、邻接链表。不同的场景及算法可能需要不同的图表示方式,一般情况下当结点数量非常庞大时,会造成矩阵非常稀疏,空间开销会较大,此时使用邻接链表的表示方式会占用较少的空间。而如果是稠密矩阵或者需要快速判断任意两个结点是否有边相连等情况,可能邻接矩阵更合适。
邻接矩阵
邻接链表
遍历
深度优先遍历 广度优先遍历
用途
商品分类选择
算法
LRU
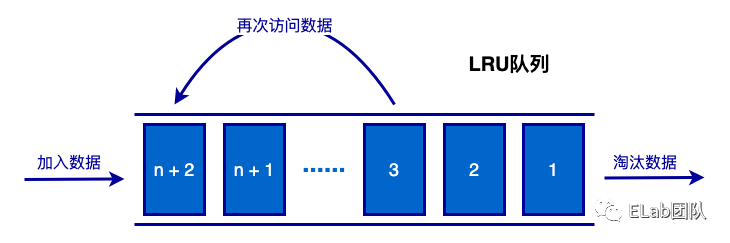
LRU 是 Least Recently Used 的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,将最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。
核心的思想就是“如果数据最近被访问,那么将来被访问的几率也就更高”。
原理
实现
思路分析:
选择合适的数据结构。
哈希表:O(1) 级别的时间复杂度,适合数据查找。但是元素无序,没办法判断元素访问的先后顺序。 数组:元素的插入和删除元素都是 O(n)。 单向链表:删除节点需要访问前驱节点,需要花 O(n)从前遍历查找。 双向链表:结点有前驱指针,删除和移动节点都是指针的变动,都是 O(1)。
结论:哈希表 + 双向链表。
使用哈希表的目的就是快速访问到存储在双向链表中的数据,存储双向链表的 key 和节点的引用;使用双向链表的目的就是快速进行节点位置的移动和删除,存储 key 和对应的数据。
设置虚拟节点,方便快速的访问头尾节点。初始时没有添加真实的节点,所以需要将虚拟节点的前驱指针和后继指针指向自己。
get 方法的实现。
put 方法的实现。
写入新数据,需要先检查一下当前节点数量;如果节点数量达到容量的最大值,则需要先删除链表尾部的节点,然后创建新的节点,添加到链表头部,并写入到哈希表。 写入已存在的数据,则更新数据值,移动节点位置到链表头部。
function Node(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
class LRUCache {
constructor(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity; // 容量
this.hash = {}; // 哈希表
this.count = 0; // 当前节点数量
this.virtualNode = new Node(); // 虚拟结点
// 相互引用
this.virtualNode.next = this.virtualNode;
this.virtualNode.prev = this.virtualNode;
}
get(key) {
const node = this.hash[key];
if (node) {
this.moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
}
put(key, value) {
const node = this.hash[key];
if (node) {
node.value = value;
this.moveToHead(node);
} else {
if (this.count === this.capacity) {
this.removeLRUItem();
}
const newNode = new Node(key, value);
this.hash[key] = newNode;
this.addToHead(newNode);
this.count++;
}
}
remove(key) {
const node = this.hash[key];
if (node) {
this.removeFromList(node);
Reflect.deleteProperty(this.hash, key);
this.count--;
}
}
isEmpty() {
return this.count === 0;
}
moveToHead(node) {
this.removeFromList(node);
this.addToHead(node);
}
removeFromList(node) {
const prevNode = node.prev;
const nextNode = node.next;
prevNode.next = nextNode;
nextNode.prev = prevNode;
node.prev = null;
node.next = null;
}
addToHead(node) {
const nextNode = this.virtualNode.next;
this.virtualNode.next = node;
nextNode.prev = node;
node.prev = this.virtualNode;
node.next = nextNode;
}
removeLRUItem() {
const tailNode = this.virtualNode.prev;
this.remove(tailNode.key);
}
}
const cache = new LRUCache(5);
console.log(cache.isEmpty());
cache.put('A', 'A');
cache.put('B', 'B');
cache.put('C', 'C');
cache.put('D', 'D');
cache.put('E', 'E');
console.log(cache.get('A'));
cache.put('F', 'F');
console.log(cache.get('B'));
console.log(cache.isEmpty());
cache.remove('E');
cache.remove('F');
cache.remove('A');
cache.remove('C');
cache.remove('D');
console.log(cache.isEmpty());
console.log(cache);
用途
历史浏览记录。 缓存淘汰策略。
我们来自字节跳动,是旗下大力教育前端部门,负责字节跳动教育全线产品前端开发工作。
我们围绕产品品质提升、开发效率、创意与前沿技术等方向沉淀与传播专业知识及案例,为业界贡献经验价值。包括但不限于性能监控、组件库、多端技术、Serverless、可视化搭建、音视频、人工智能、产品设计与营销等内容。
欢迎感兴趣的同学在评论区或使用内推码内推到作者部门拍砖哦 🤪
字节跳动校/社招投递链接: https://job.toutiao.com/s/eGrF9qQ
