如何写好 Java 业务代码?这也是有很多规范的!
为什么要写好业务代码?
API如何拒绝烟囱式开发
上述的api开发开发过程就是典型的烟囱式开发模式,所有的api服务与相似业务,但是每个api都是完全独立的开发,其开发流程如图:
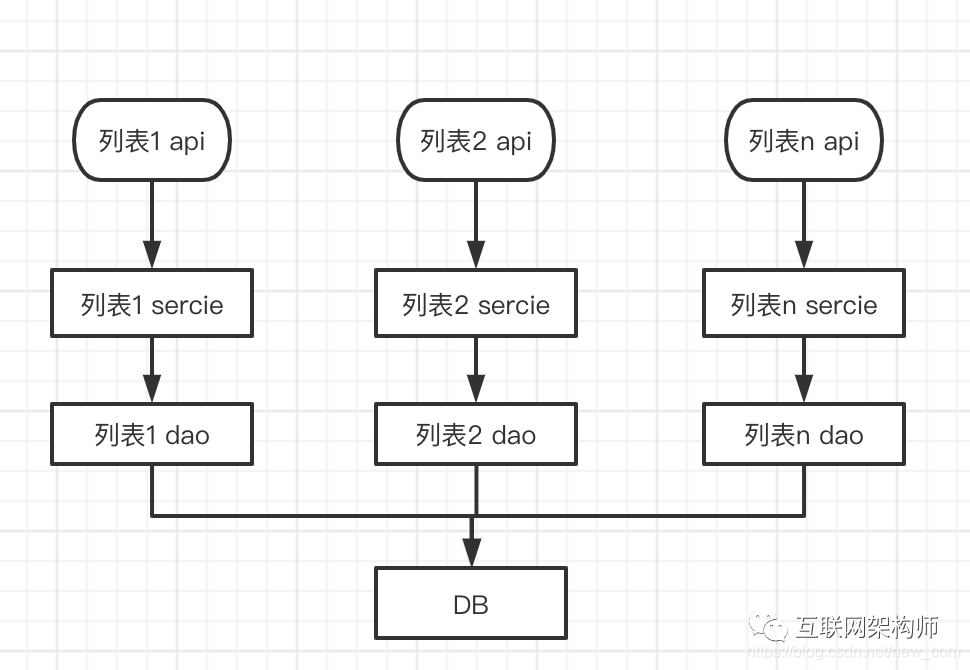
业务代码重复,在不同的service实现中,业务相似的话会有大量重复代码。
数据库表结构的改动需要修改所有涉及到的dao层,维护成本比较高。
此类相似业务,api层定义各自显示对象,dao层负责获取全量数据(例如,用户查询,就获取整个用户表字段的数据),service层定义业务对象,根据不同api不同业务类型的判断,根据dao查询的数据组转业务对象,以及业务对象向api显示对象的转换。
开发流程如图:
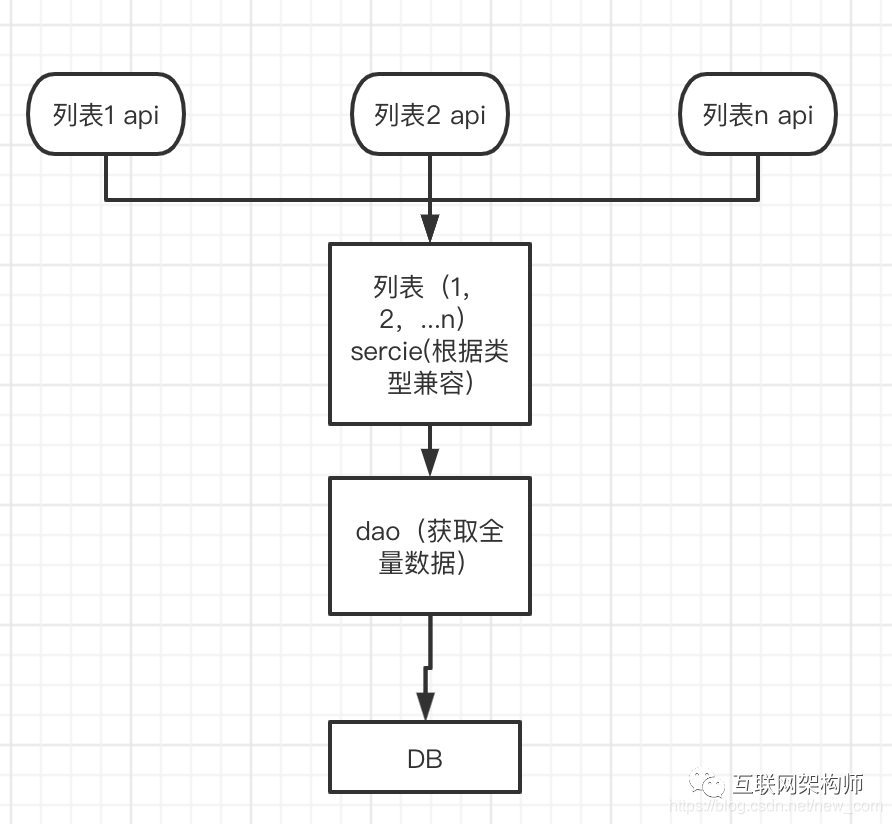
这样的开发模式有如下优势:
业务代码集中在service层,专注业务对象bo的封装,以及业务对象向给类显示层vo的转换;封装复用逻辑,可以大量减少重复代码。如果,设计模式从一开始就设计得易扩展,后期维护就快捷的多。
业务代码如何拒绝All in one?
权限校验:
使用aop对权限校验逻辑进行抽取,能够通过注解的方式指定哪些controller需要进行权限校验。对用户进行数据过滤时,使用controller的拦截器获取该用户拥有的各类权限,并把用户数据保存在上下文threadloal中,并且通过配置对指定url进行拦截。在业务层,从上下文拿到用户权限数据做各类数据业务过滤,通过aop实现各类拦截业务的指定调用。
参数校验:
使用java validtion对通用的字段,例如电话号码,身份证,进行扩展,详细可以参考,如何使用validation校验参数?,在项目中其他类似校验进行复用。
业务判断:使用设计模式对不同类型的业务开发进行封装,集成,多态扩展;这样在后期的扩展中可以基于开发封闭原则,针对新的业务扩展子类即可。
业务对象转换数:
业务开发过程中,依照阿里巴巴研发规范的要求,存在DO(数据库表结构一致的对象),BO(业务对象),DTO(数据传输对象),VO(显示层对象),Query(查询对象)。
使用MapStruct,可以灵活的控制的不同属性值之间的转换规格,比org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties()方法更加灵活。
示例:
public interface CategoryConverter {
CategoryConverter INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(CategoryConverter.class);
@Mappings({
@Mapping(target = "ext", expression = "java(getCategoryExt(updateCategoryDto.getStyle(),updateCategoryDto.getGoodsPageSize()))")})
Category update2Category(UpdateCategoryDto updateCategoryDto);
@Mappings({
@Mapping(target = "ext", expression = "java(getCategoryExt(addCategoryDto.getStyle(),addCategoryDto.getGoodsPageSize()))")})
Category add2Category(AddCategoryDto addCategoryDto);
}
DB数据库公共字段填充:
例如,公共字段,生成日期,创建人,修改时间,修改人使用插件的形式进行封装,在mybatis-plus中使用MetaObjectHandler,在执行sql之前完成统一字段值的填充。
业务平台字段查询过滤:
在中台的开发中,数据采用不同平台code的列实现不同平台业务数据的隔离。基于mybatis插件机制的多租户过滤机制实现可以参考如何使用MyBatis的plugin插件实现多租户的数据过滤?。
在dao层的方法或者接口上加上自定义过滤条件即可,示例如下:
@Mapper
@Repository
@MultiTenancy(multiTenancyQueryValueFactory = CustomerQueryValueFactory.class)
public interface ProductDao extends BaseMapper<Product> {
}
缓存的使用:
Spring开发中通常集成spring cache使用以注解的形式使用缓存。整合redis并且自定义默认时间设置可以参考(Spring Cache+redis自定义缓存过期时间)。
示例如下:
/**
* 使用CacheEvict注解更新指定key的缓存
*/
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = {ALL_PRODUCT_KEY,ONLINE_PRODUCT_KEY}, allEntries = true)
public Boolean add(ProductAddDto dto) {
// TODO 添加商品更新cache
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {ALL_PRODUCT_KEY})
public List<ProductVo> findAllProductVo() {
return this.baseMapper.selectList(null);
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value = {ONLINE_PRODUCT_KEY})
public ProductVo getOnlineProductVo() {
// TODO 设置查询条件
return this.baseMapper.selectList(query);
}
枚举类的使用:
在业务中特别是状态的值,在对外发布api的vo对象中,加上状态枚举值的注释,并且使用@link 注解,可以直接连接到枚举类,让开发者一目了然。
示例如下:
public class ProductVo implements Serializable { /**
* 审核状态
* {@link ProductStatus}
*/
@ApiModelProperty("状态")
private Integer status;
}
迁移sql查询条件:
避免在sql层写固定的通用的过滤条件,迁移到服务层做处理。
示例如下:
// sql查询条件
SELECT * from product
where status != -1 and shop_status != 6
// 在业务层把各类状态值进行条件设置
public PageData<ProductVo> findCustPage(Query query ){
// 产品上线,显示状态
query.setStatus(ProductStatus.ONSHELF);
// 产品显示状态
query.setHideState(HideState.VISIBAL);
// 店铺未下线
query.setNotStatus(ShopStatus.OFFLINE);
return productService.findProductVoPage(query);
}
加分项的规范
乐观锁与悲观锁的使用
阿里的《Java开发手册》建议看下。乐观锁(使用Spring AOP+注解基于CAS方式实现java的乐观锁)设置重试次数以及重试时间,在简单的对象属性修改使用乐观锁,示例如下:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
@OptimisticRetry
public void updateGoods(GoodsUpdateDto dto) {
Goods existGoods = this.getGoods(dto.getCode());
// 属性逻辑判断 //
if (0 == goodsDao.updateGoods(existGoods, dto)) {
throw new OptimisticLockingFailureException("update goods optimistic locking failure!");
}
}
@Transactional
public void updateProduct(Long id,ProductUpdateDto dto){
Product existingProduct;
// 根据产品id对数据加锁
Assert.notNull(existingProduct = lockProduct(id), "无效的产品id!");
// TODO 逻辑条件判断
// TODO 修改商品属性,名称,状态
// TODO 修改价格
// TODO 修改库存
// TODO 修改商品规格
}
读写分离的使用
开发中,经常使用mybatisplus实现读写分离。常规的查询操作,就走从库查询,查询请求可以不加数据库事务,例如列表查询,示例如下:
@Override
@DS("slave_1")
public List<Product> findList(ProductQuery query) {
QueryWrapper<Product> queryWrapper = this.buildQueryWrapper(query);
return this.baseMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
}
示例,产品下线时,使用reids生成日志code,产品相关写操作执行完成后,发送消息,代码如下:
public void offlineProduct(OfflineProductDto dto){
// TODO 修改操作为涉及到的查询操作
// TODO 使用redis生成业务code
// 使用声明式事务控制产品状态修改的相关数据库操作
boolean status = transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallback<Boolean>() {
@Nullable
@Override
public Boolean doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
try {
// TODO 更改产品状态
} catch (Exception e) {
status.setRollbackOnly();
throw e;
}
return true;
}
});
// TODO 使用消息中间件发送消息
}
数据库自动给容灾
结合配置中心,简单实现数据库的自动容灾。以nacous配置中心为例,如何使用Nacos实现数据库连接的自动切换?。
在springboot启动类加上@EnableNacosDynamicDataSource配置注解,即可无侵入的实现数据库连接的动态切换,示例如下:
@EnableNacosDynamicDataSource
public class ProductApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProductApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试用例的编写
基于TDD的原则,结合junit和mockito实现服务功能的测试用例,为什么要写单元测试?基于junit如何写单元测试?。添加或者修改对象时,需要校验入参的有效性,并且校验操作以后的对象的各类属性。
以添加类目的api测试用例为例,如下,添加类别,成功后,校验添加参数以及添加成功后的属性,以及其他默认字段例如状态,排序等字段,源码如下:
// 添加类别的测试用例
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback
public void success2addCategory() throws Exception {
AddCategoryDto addCategoryDto = new AddCategoryDto();
addCategoryDto.setName("服装");
addCategoryDto.setLevel(1);
addCategoryDto.setSort(1);
Response<CategorySuccessVo> responseCategorySuccessVo = this.addCategory(addCategoryDto);
CategorySuccessVo addParentCategorySuccessVo = responseCategorySuccessVo.getData();
org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull(addParentCategorySuccessVo);
org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull(addParentCategorySuccessVo.getId());
org.junit.Assert.assertEquals(addParentCategorySuccessVo.getPid(), ROOT_PID);
org.junit.Assert.assertEquals(addParentCategorySuccessVo.getStatus(), CategoryEnum.CATEGORY_STATUS_DOWN.getValue());
org.junit.Assert.assertEquals(addParentCategorySuccessVo.getName(), addCategoryDto.getName());
org.junit.Assert.assertEquals(addParentCategorySuccessVo.getLevel(), addCategoryDto.getLevel());
org.junit.Assert.assertEquals(addParentCategorySuccessVo.getSort(), addCategoryDto.getSort());
}
// 新增类目,成功添加后,返回根据id查询CategorySuccessVo
public CategorySuccessVo add(AddCategoryDto addCategoryDto, UserContext userContext) {
Category addingCategory = CategoryConverter.INSTANCE.add2Category(addCategoryDto);
addingCategory.setStatus(CategoryEnum.CATEGORY_STATUS_DOWN.getValue());
if (Objects.isNull(addCategoryDto.getLevel())) {
addingCategory.setLevel(1);
}
if (Objects.isNull(addCategoryDto.getSort())) {
addingCategory.setSort(100);
}
categoryDao.insert(addingCategory);
return getCategorySuccessVo(addingCategory.getId());
}
也需要对添加类目的参数进行校验,例如,名称不能重复的校验,示例如下:
// 添加类目的入参
public class AddCategoryDto implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4752897765723264858L;
// 名称不能为空,名称不能重复
@NotEmpty(message = CATEGORY_NAME_IS_EMPTY, groups = {ValidateGroup.First.class})
@EffectiveValue(shouldBeNull = true, message = CATEGORY_NAME_IS_DUPLICATE, serviceBean = NameOfCategoryForAddValidator.class, groups = {ValidateGroup.Second.class})
@ApiModelProperty(value = "类目名称", required = true)
private String name;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "类目层级")
private Integer level;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "排序")
private Integer sort;
}
//添加失败的校验校验测试用例
@Test
public void fail2addCategory() throws Exception {
AddCategoryDto addCategoryDto = new AddCategoryDto();
addCategoryDto.setName("服装");
addCategoryDto.setLevel(1);
addCategoryDto.setSort(1);
// 名称为空
addCategoryDto.setName(null);
Response<CategorySuccessVo> errorResponse = this.addCategory(addCategoryDto);
org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull(errorResponse);
org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull(errorResponse.getMsg(), CATEGORY_NAME_IS_EMPTY);
addCategoryDto.setName("服装");
// 成功添加类目
this.addCategory(addCategoryDto);
// 名称重复
errorResponse = this.addCategory(addCategoryDto);
org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull(errorResponse);
org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull(errorResponse.getMsg(), CATEGORY_NAME_IS_DUPLICATE);
}
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/new_com/article/details/108399421
正文结束
1.救救大龄码农!45岁程序员在国务院网站求助总理!央媒网评来了...
5.37岁程序员被裁,120天没找到工作,无奈去小公司,结果懵了...

