牛逼!硬核图解 Tomcat 整体架构
相关阅读:2T架构师学习资料干货分享

处理 socket 连接,负责将网络字节流与 Request 和 Response 对象的转化;
加载和管理 Servlet,以及具体处理 Request 请求;
Tomcat 支持的 io 模型有 NIO、NIO2、APR,Tomcat 支持的应用层协议有 http1.1 ajp http2.0。
通过组合模式、模板方法、观察者模式和骨架抽象类,tomcat 定义了基类 LifeCycleBean 实现 LifeCycle 接口,把公共的逻辑,生命周期状态转变和维护、生命事件的触发和监听器的添加删除,子类负责实现自己的 init、stop 和 start 等方法。
tomcat 自定义了监听器; @WebListener 注解,定义自己的监听器;
StandardServer、StandardService 等是 Server 和 Service 组件的具体实现类,它们都继承了 LifecycleBase。
StandardEngine、StandardHost、StandardContext 和 StandardWrapper 是相应容器组件的具体实现类,因为它们都是容器,所以继承了 ContainerBase 抽象基类,而 ContainerBase 实现了 Container 接口,也继承了 LifecycleBase 类,它们的生命周期管理接口和功能接口是分开的。
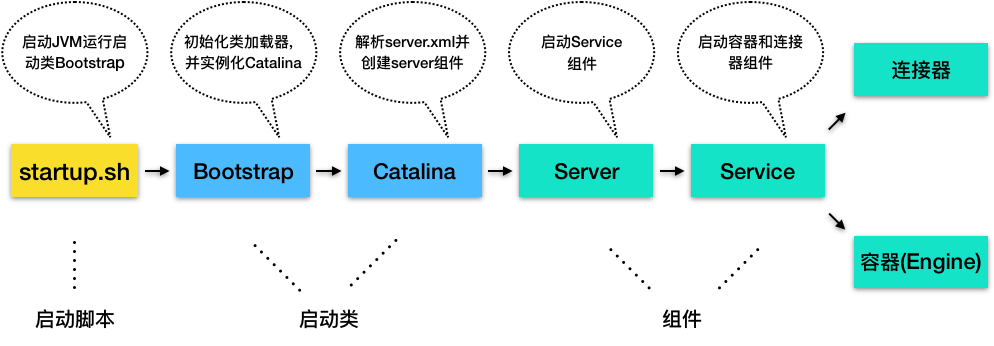
连接器 Connector
监听网络端口; 接受网络请求; 读取网络字节流; 根据应用层协议解析字节流,生成统一的 tomcat request 和 tomcat response 对象; 将 tomcat request 对象转成 servletRequest; 调用 servlet 容器,得到 servletResponse; 将 servletResponse 转成 tomcat response; 将 tomcat response 转成网络字节流; 将响应字节流写回给浏览器;
网络通信; 应用层协议解析; tomcat request/response 与 servlet request/response 的转换;
组件通过接口交互,好处是封装变化。
Endpoint 负责提供字节流给 Processor,Processor 负责提供 tomcat request 对象给 Adapter,Adapter负责提供 Servlet Request 给容器。
其中 Endpoint 和 Processor 抽象组装在一起形成了 ProtocolHandler 组件。
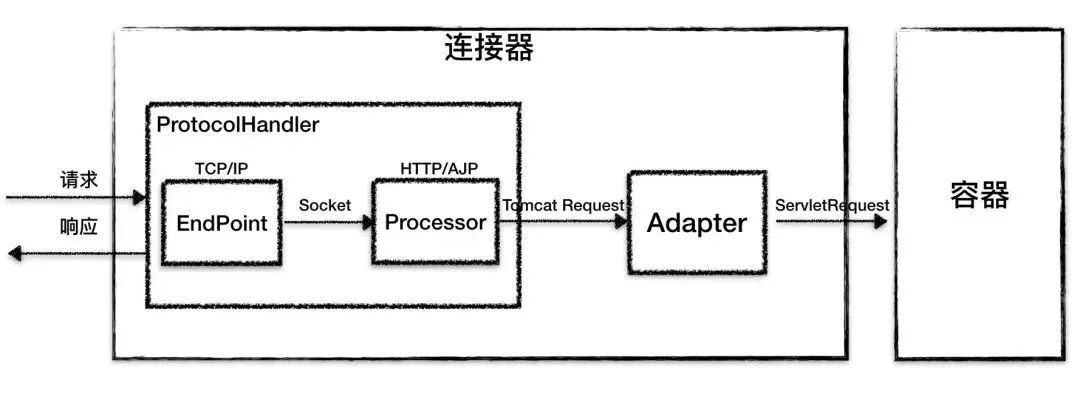
ProtocolHandler
Endpoint
接口,抽象实现类是 AbstractEndpoint,具体子类在 NioEndpoint 和 Nio2Endpoint,其中两个重要组件:Acceptor 和 SocketProcessor。
Acceptor 用于监听 Socket 连接请求,SocketProcessor 用于处理收到的 Socket 请求,提交到线程池 Executor 处理。
Processor
接收 Endpoint 的 socket,读取字节流解析成 tomcat request 和 response,通过 adapter 将其提交到容器处理。Processor 的具体实现类 AjpProcessor、Http11Processor 实现了特定协议的解析方法和请求处理方式。
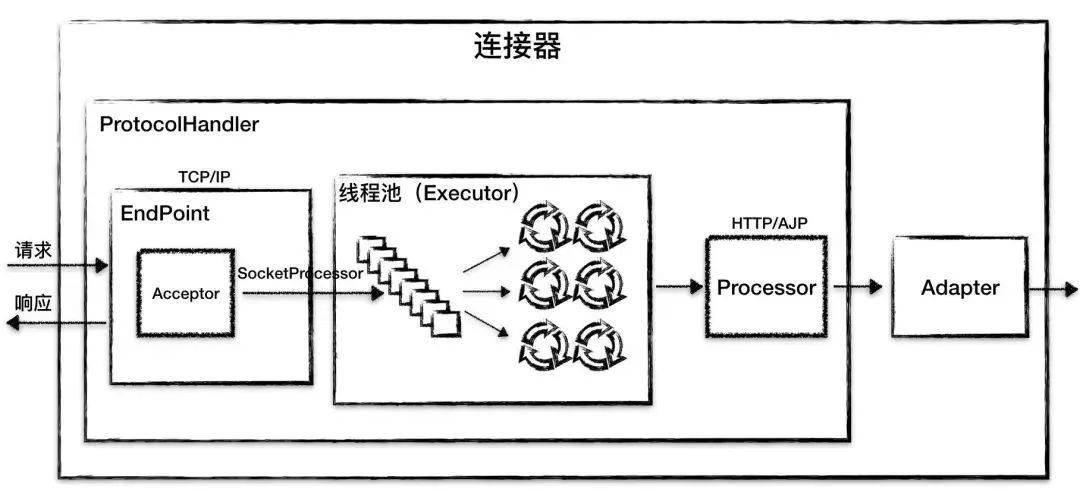
Endpoint 接收到 socket 连接后,生成一个 socketProcessor 交给线程池处理,run 方法会调用 Processor 解析应用层协议,生成 tomcat request 后,调用 adapter 的 service 方法。
Adapter
ProtocolHandler 接口负责解析请求生成 tomcat requst,CoyoteAdapter 的 service 方法,将 Tomcat Request 对象,转成 ServletRequest,再调用 service 方法。
容器 Container
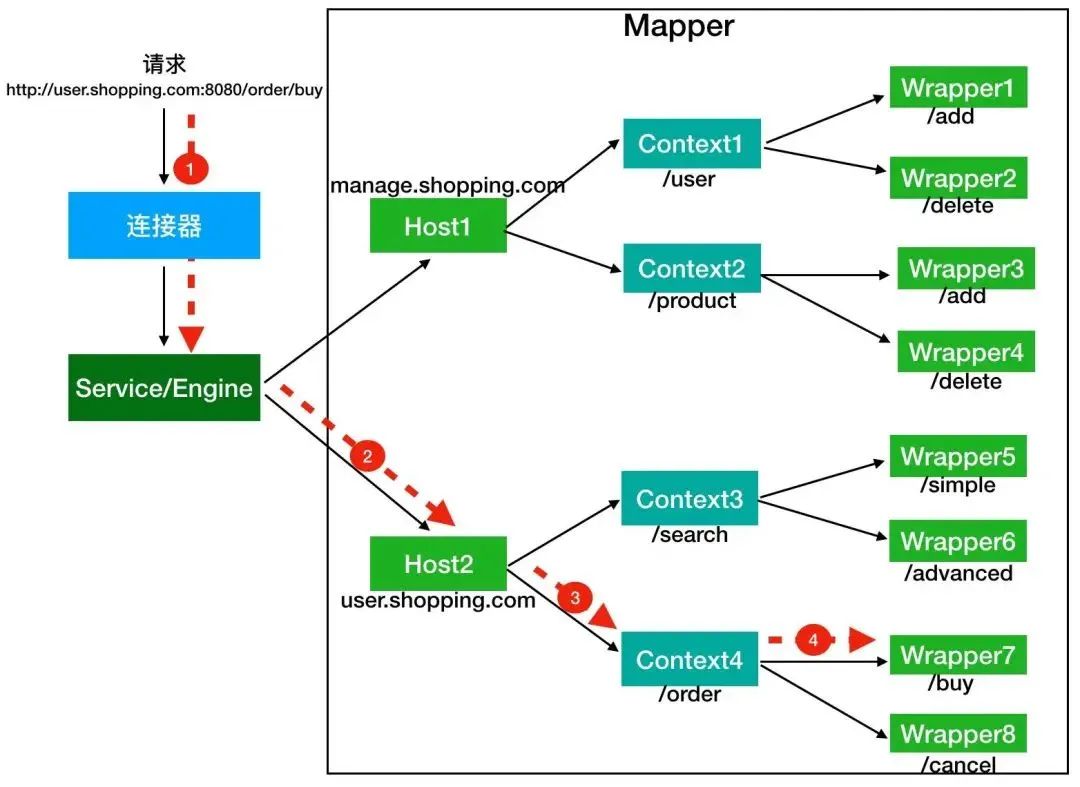
容器的层次结构
父子关系的 Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper 和 Servlet。Context 表示 web 应用程序、wrapper 表示 servlet、context 有多个 wrapper,host 也有多个 context。另外搜索公众号互联网架构师回复关键字"2T”获取一份惊喜礼包。
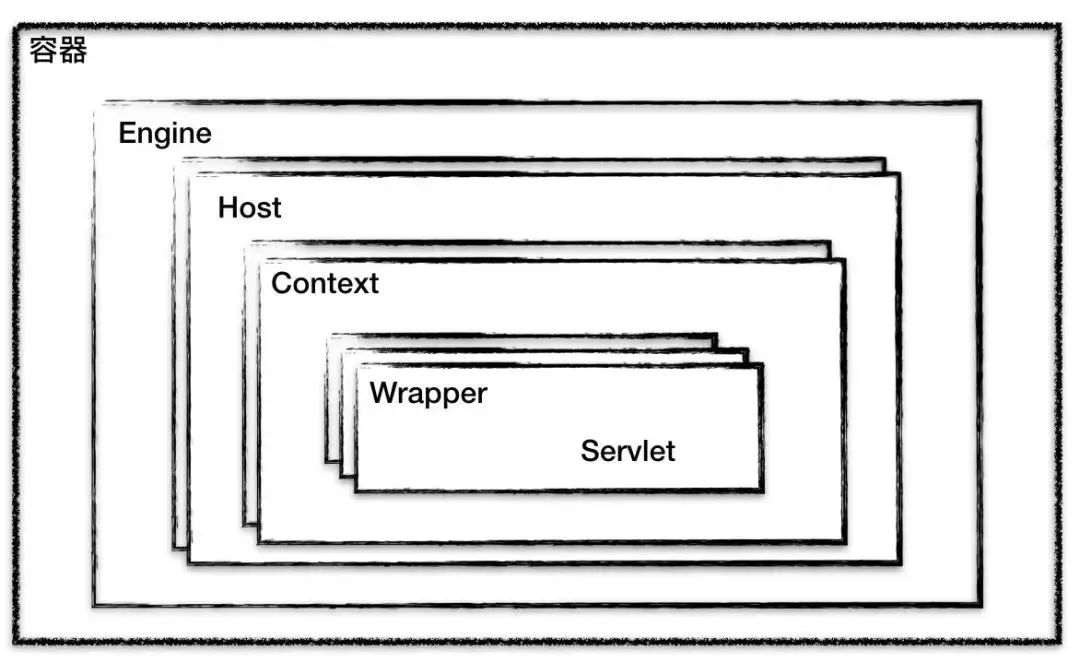
Host 代表的是一个虚拟主机,或者说一个站点,可以给 Tomcat 配置多个虚拟主机地址,而一个虚拟主机下可以部署多个 Web 应用程序;Engine 表示引擎,用来管理多个虚拟站点,一个 Service 最多只能有一个 Engine。
容器通过 Pipeline-Valve 责任链,对请求一次处理,invoke 处理方法,每个容器都有一个 Pipeline,触发第一个 Valve,这个容器的 valve 都会被调到,不同容器之间通过 Pipeline 的 getBasic 方法,负责调用下层容器的第一个 Valve。
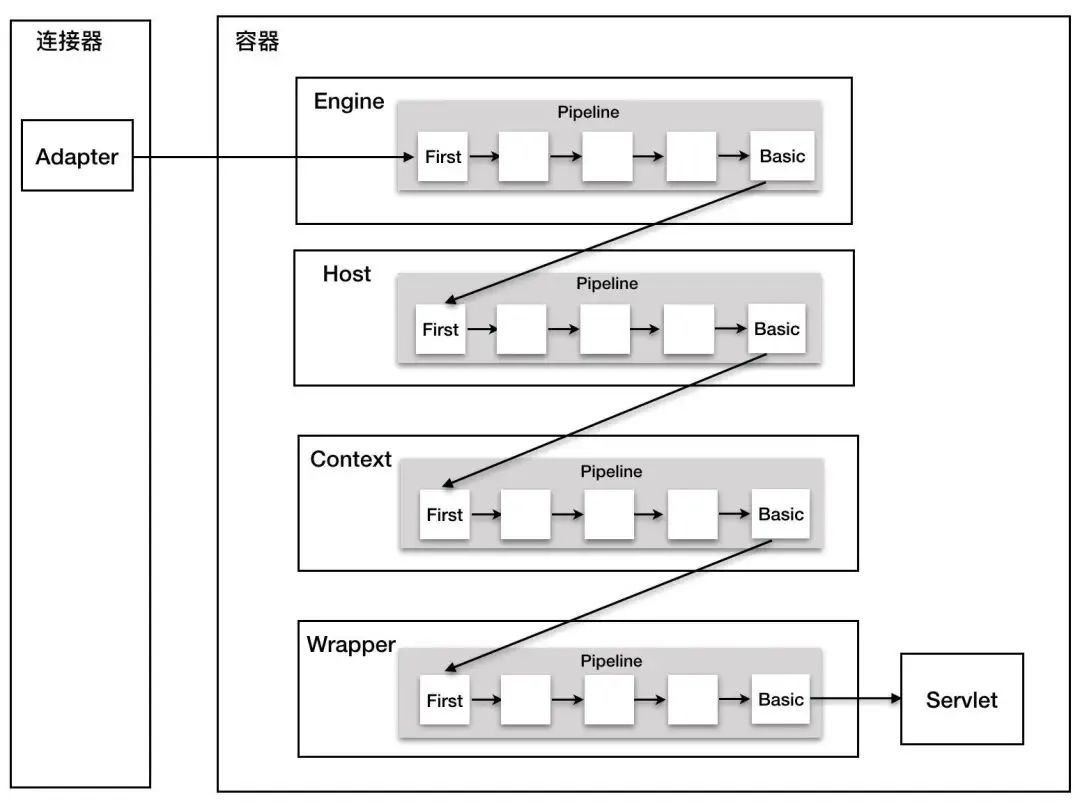
整个调用连由连接器中的 adapter 触发,调用 engine 中的第一个 Valve。
1// Calling the container
2connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
wrapper 容器的最后一个 valve 创建一个 filter 链,并调用 doFilter 方法,最终会调用到 servlet 的 service 方法。
1final class StandardWrapperValve
2 extends ValveBase {
3
4 @Override
5 public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
6 throws IOException, ServletException {
7 // ...
8
9 ApplicationFilterChain filterChain =
10 ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
11
12 // Call the filter chain for this request
13 // NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method
14 Container container = this.container;
15 try {
16 if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
17 // Swallow output if needed
18 if (context.getSwallowOutput()) {
19 try {
20 SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
21 if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
22 request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
23 } else {
24
25 // dofilter
26 filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(),
27 response.getResponse());
28 }
29 } finally {
30 String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
31 if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
32 context.getLogger().info(log);
33 }
34 }
35 } else {
36 if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) {
37 request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();
38 } else {
39 // dofilter
40 filterChain.doFilter
41 (request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
42 }
43 }
44
45 }
46 } catch() {
47 // ...
48 }
49 }
50}ServletContext 是 tomcat 中的一个成员变量,spring 中的 ApplicationContext 是 servlet 规范中的 ServletContext 属性。
