Go 刷 leetcode|智慧树下你和我
今天为大家讲解 LeetCode 第 94 题,仍然继续分享一道树的题目。
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序 遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3] 1
2 / 3输出: [1,3,2] 进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
先简单介绍下树的前中后序遍历。
无论是哪种遍历方法,考查节点的顺序都是一样的(思考做试卷的时候,人工遍历考查顺序)。只不过有时候考查了节点,将其暂存,需要之后的过程中输出。
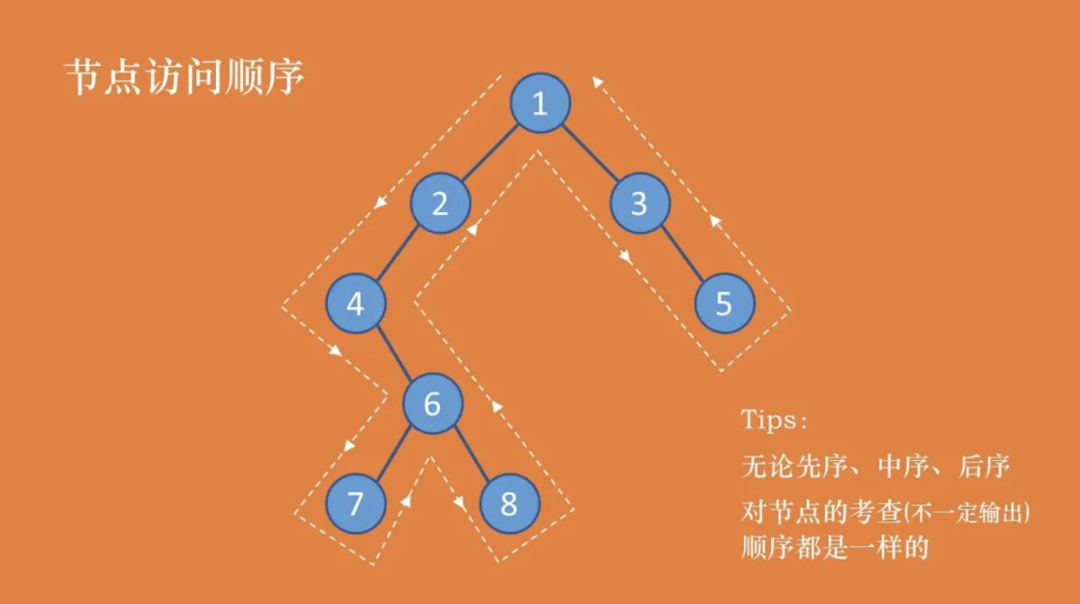
如上图所示,三种遍历方法(人工)得到的结果分别是:
先序:1 2 4 6 7 8 3 5 中序:4 7 6 8 2 1 3 5 后序:7 8 6 4 2 5 3 1
三种遍历方法的考查顺序一致,得到的结果却不一样,原因在于:
先序:考察到一个节点后,即刻输出该节点的值,并继续遍历其左右子树。(根左右)
中序:考察到一个节点后,将其暂存,遍历完左子树后,再输出该节点的值,然后遍历右子树。(左根右)
后序:考察到一个节点后,将其暂存,遍历完左右子树后,再输出该节点的值。(左右根)
方法一:递归
树的结构具有天然的递归性,使用递归还是比较容易的。不多说上代码。
//go
//* Definition for a binary tree node.
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
var res []int
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
res = make([]int, 0)
inorder(root)
return res
}
func inorder(root *TreeNode) {
if root != nil {
inorder(root.Left)
res = append(res, root.Val)
inorder(root.Right)
}
}
//java
class Solution {
public List < Integer > inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List < Integer > res = new ArrayList < > ();
helper(root, res);
return res;
}
public void helper(TreeNode root, List < Integer > res) {
if (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) {
helper(root.left, res);
}
res.add(root.val);
if (root.right != null) {
helper(root.right, res);
}
}
}
}
方法二:遍历
这是在题解中看到一个不错也挺好理解的优化方法,这里分享一下@henry
其核心思想如下:
使用颜色标记节点的状态,新节点为白色,已访问的节点为灰色。 如果遇到的节点为白色,则将其标记为灰色,然后将其右子节点、自身、左子节点依次入栈。 如果遇到的节点为灰色,则将节点的值输出。
如要实现前序、后序遍历,只需要调整左右子节点的入栈顺序即可。
//go
type ColorNode struct {
node *TreeNode
color string
}
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
var res []int
var stack []*ColorNode
stack = append(stack, &ColorNode{root, "white"})
var cn *ColorNode
for len(stack) != 0 {
cn = stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1] // 以上两句等同于 cn = stack.pop() ,别忘了加这句
if cn.color == "white" {
// 因为栈是先进后出,所以中序是 右-根-左 的顺序添加
if cn.node.Right != nil {
stack = append(stack, &ColorNode{cn.node.Right,"white"})
}
stack = append(stack,&ColorNode{cn.node, "gray"})
if cn.node.Left != nil {
stack = append(stack, &ColorNode{cn.node.Left, "white"})
}
}else {
res = append(res, cn.node.Val)
}
}
return res
}
//java
class Solution {
class ColorNode {
TreeNode node;
String color;
public ColorNode(TreeNode node,String color){
this.node = node;
this.color = color;
}
}
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new ArrayList();
List res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new ColorNode(root,"white"));
while(!stack.empty()){
ColorNode cn = stack.pop();
if(cn.color.equals("white")){
if(cn.node.right != null) stack.push(new ColorNode(cn.node.right,"white"));
stack.push(new ColorNode(cn.node,"gray"));
if(cn.node.left != null)stack.push(new ColorNode(cn.node.left,"white"));
}else{
res.add(cn.node.val);
}
}
return res;
}
}
郑重声明:
所展示代码已通过 LeetCode 运行通过,请放心食用~
推荐阅读
站长 polarisxu
自己的原创文章
不限于 Go 技术
职场和创业经验
Go语言中文网
每天为你
分享 Go 知识
Go爱好者值得关注
