Mybatis 代理方式运行原理与总结

点击上方「Java有货」关注我们

+
引言
本文主要是对Mybatis SqlSessionFactory 初始化原理和Mybatis SqlSession执行流程 的总结与扩展,没有月的小伙伴,可以先阅读这脸皮文章哦!
代理方式源码分析
回顾代理模式的写法:
/*** mapper代理方式*/public void test2() throws IOException {InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();// 使用JDK动态代理对mapper接口产生代理对象IUserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserMapper.class);//代理对象调用接口中的任意方法,执行的都是动态代理中的invoke方法List<Object> allUser = mapper.findAllUser();}
这里我们就需要带着问题去看源码
SqlSession是如何生成接口的代理对象的
代理对象执行方法时(
invoke),是如何进行一些处理的
getMapper()源码解析
我们看getMapper()之前,首先思考一下,使用代理模式开发,需要怎么做?
创建Dao接口,编写方法,编写对应的
mapper映射文件在核心配置类中扫描Dao接口,一般是使用扫描包的形式
所以,我们先去看解析核心配置中mappers标签的源码,看看扫描后,他是将我们配置的类放到了哪里?
通过Mybatis初始化过程的源码分析,我们直接来到XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement()方法
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {if (parent != null) {// 遍历子节点for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {// 如果是 package 标签,则扫描该包if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {// 获得包名String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");// 添加到 configuration 中configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);// 如果是 mapper 标签,} else {// ···}}}}
这里可以看到,如果扫描包的形式,会调用configuration.addMappers()方法
public class MapperRegistry {/*** MapperProxyFactory 的映射** KEY:Mapper 接口*///这个类中维护一个HashMap存放MapperProxyFactoryprivate final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();public void addMappers(String packageName) {addMappers(packageName, Object.class);}/*** 扫描指定包,并将符合的类,添加到 {@link #knownMappers} 中** @since 3.2.2*/public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {// 扫描指定包下的指定类ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();// 遍历,添加到 knownMappers 中for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {addMapper(mapperClass);}}public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {// 判断,必须是接口。if (type.isInterface()) {// 已经添加过,则抛出 BindingException 异常if (hasMapper(type)) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");}boolean loadCompleted = false;try {// 添加到 knownMappers 中knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));// 解析 Mapper 的注解配置MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);parser.parse();// 标记加载完成loadCompleted = true;} finally {// 若加载未完成,从 knownMappers 中移除if (!loadCompleted) {knownMappers.remove(type);}}}}}
通过源码,我们发现了Mybatis会获取包下所有类对象Class,然后通过new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)创建出代理工厂对象,Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers存放到Map中
key:类对象
value:
MapperProxyFactory代理工厂对象
到此,我们就知道了,在Mybatis初始化过程中,会将配置的Dao类保存到Map中
接着,我们去查看getMapper()源码
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {return configuration.getMapper(type, this);}public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);}("unchecked")public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {// 获得 MapperProxyFactory 对象final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);// 不存在,则抛出 BindingException 异常if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}/// 通过动态代理工厂生成实例。try {return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}
最终就来到了MapperRegistry对象中,也就是刚刚注册Dao接口的地方,通过源码会发现,他先从Map中取出该类对应的MapperProxyFactory,然后调用mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession)来构建代理对象
/*** Mapper Proxy 工厂类** @author Lasse Voss*/public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {("unchecked")protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);}//MapperProxyFactory类中的newInstance方法public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {// 创建了JDK动态代理的invocationHandler接口的实现类mapperProxyfinal MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);// 调用了重载方法return newInstance(mapperProxy);}}
创建MapperProxy对象,这个对象实现类InvocationHandler代理必备接口
创建
MapperProxy对象,这个对象实现类InvocationHandler代理必备接口通过JDK动态代理的方式,构建出Dao对应的代理对象并返回,所以,通过源码,我们最终知道了:
Mybatis初始化时,会扫描配置的包,把Dao接口和对应的
MapperProxyFactory以键值对形式保存到Map中通过getMapper()获取代理对象时,是使用JDK动态代理的形式创建出了
MapperProxy代理对象
invoke()源码分析
通过前面的学习,我们知道代理类不管执行什么方法,都会走invoke()方法,所以我们直接取MapperProxy查看invoke方法的源码
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//····// 获得 MapperMethod 对象final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);// 重点在这:MapperMethod最终调用了执行的方法return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;//判断mapper中的方法类型,最终调用的还是SqlSession中的方法switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {// 转换参数Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 执行 INSERT 操作// 转换 rowCountresult = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {// 转换参数Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 转换 rowCountresult = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {// 转换参数Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 转换 rowCountresult = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:// 无返回,并且有 ResultHandler 方法参数,则将查询的结果,提交给 ResultHandler 进行处理if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;// 执行查询,返回列表} else if (method.returnsMany()) {result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);// 执行查询,返回 Map} else if (method.returnsMap()) {result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);// 执行查询,返回 Cursor} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);// 执行查询,返回单个对象} else {// 转换参数Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 查询单条result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);if (method.returnsOptional() &&(result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}// 返回结果为 null ,并且返回类型为基本类型,则抛出 BindingException 异常if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}// 返回结果return result;}
通过源码,我们可以看到,首先会判断方法类型,是增删改查中的哪一种,然后其实还是调用的SqlSession中的增删改查方法
查询方法里,会根据返回值不同进行不同的请求,我们看一下返回列表也就是List类型的方法
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {List<E> result;// 转换参数Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 执行 SELECT 操作if (method.hasRowBounds()) {RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);} else {result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);}// issue #510 Collections & arrays support// 封装 Array 或 Collection 结果if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) { // 情况一,Arrayreturn convertToArray(result);} else {return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result); // 情况二,Collection}}// 直接返回的结果return result; // 情况三,默认}
可以看到,实际还是执行的 sqlSession.selectList()方法,然后传入StatementId等参数
到这里关于Mybatis的执行流程就梳理完成了,如果您没有看到之前的文章,请放回公众号首页阅读管理Mybatis的相关文章,有助于您更好的理解执行流程
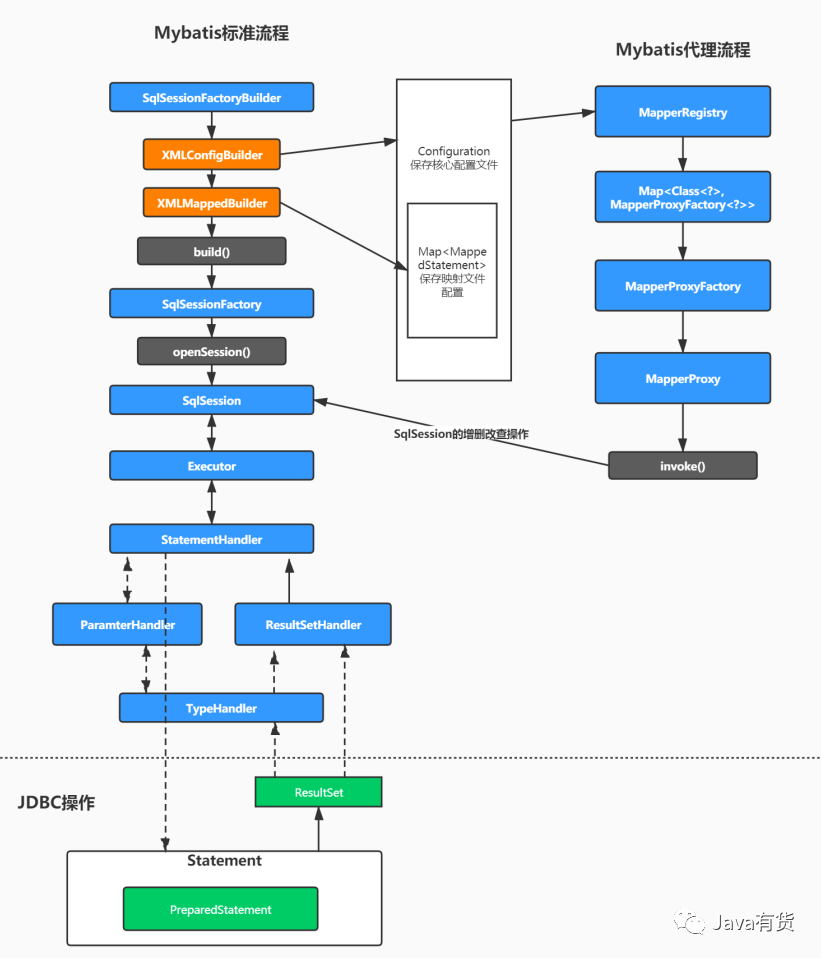
Mybatis整体流程总结