JS操作小技巧,工作简单了

一、Optional Chaining
在javaScript中,对象的属性链访问,很容易因为某一个属性不存在出现 Cannot read property 'xxx' of undefined的问题,那么Optional Chaining就添加了?.操作符,它会先判断前面的值,如果undefined或者null,就结束后面的调用,直接返回undefined;
1.1 访问深度嵌套的属性
const obj = {foo: {bar: {baz: 42,},},};const baz = obj?.foo?.bar?.baz; // 42const safe = obj?.qux?.baz; // undefined// Optional chaining and normal chaining can be intermixedobj?.foo.bar?.baz; // Only access `foo` if `obj` exists, and `baz` if// `bar` exists// Example usage with bracket notation:obj?.['foo']?.bar?.baz // 42
1.2 调用深层嵌套的函数
const obj = {foo: {bar: {baz() {return42;},},},};const baz = obj?.foo?.bar?.baz(); // 42const safe = obj?.qux?.baz(); // undefinedconst safe2 = obj?.foo.bar.qux?.(); // undefinedconst willThrow = obj?.foo.bar.qux(); // Error: not a function// Top function can be called directly, too.functiontest() {return42;}test?.(); // 42exists?.(); // undefined
1.3 构造深层嵌套的类
const obj = {foo: {bar: {baz: class{},},},};const baz = new obj?.foo?.bar?.baz(); // baz instanceconst safe = new obj?.qux?.baz(); // undefinedconst safe2 = new obj?.foo.bar.qux?.(); // undefinedconst willThrow = new obj?.foo.bar.qux(); // Error: not a constructor// Top classes can be called directly, too.classTest{}new Test?.(); // test instancenew exists?.(); // undefined
1.4 安装使用
安装:
npminstall--save-dev @babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chainingyarn add @babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chaining --dev
配置.babelrc:
{"plugins": ["@babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chaining"]}复制
二、随机生成字母和数组的组合
Math.random().toString(36).substr(2);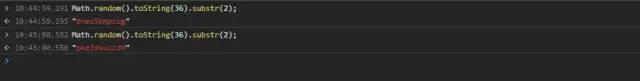
三、转换布尔值
const isTrue = !0;const isFalse = !1;const alsoFalse = !!0;console.log(isTrue); // Result: trueconsole.log(typeoftrue); // Result: "boolean"
四、转换数字
constnumber = '10';number = +number;console.log(number); // 10
constnumber = '10';number = ~~number;console.log(number); // 10
五、替代Math.pow
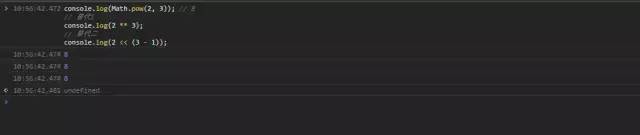
console.log(Math.pow(2, 3));// 替代1console.log(2 ** 3);// 替代二,只能以二作为基数console.log(2 << (3 - 1));
六、快速浮点数转整数
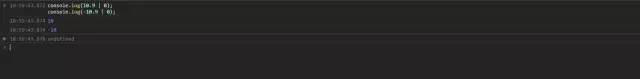
console.log(10.9 | 0); // 10console.log(-10.9 | 0); // 10
console.log(~~10.9);console.log(~~-10.9);

七、数组降维度
二维数组
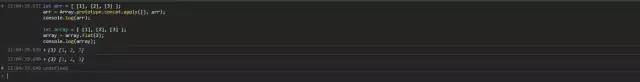
let arr = [ [1], [2], [3] ];arr = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr);console.log(arr);// [1, 2, 3]let array = [ [1], [2], [3] ];array = array.flat(2);console.log(array); // [1, 2, 3]
多维数组
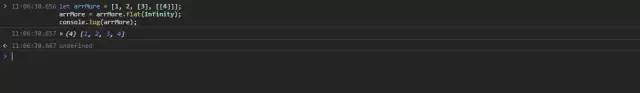
let arrMore = [1, 2, [3], [[4]]];arrMore = arrMore.flat(Infinity);console.log(arrMore);
八、判断小数是否相等
console.log(0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3); // falsefunctionequal(number1, number2) {returnMath.abs(number1 - number2) < Math.pow(2, -52);}console.log(equal(0.1 + 0.2, 0.3));

九、判断变量是否是数组
1.instanceof2.array.__proto__.constructor === Array3.array.constructor === Array4.Array.isArray(兼容性问题)5. Object.prototype.toString.call([]) === "[object Array]"(最通用)
PS:instanceof和constructor判断的变量,必须在当前页面声明。例如:父页面是一个框架,框架中引入一个页面(子页面),在子页面中申明的array,并将其复制给父元素的一个变量,这时instanceof和constructor判断该变量,将返回false。----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 原因:array是复合类型。在传递的过程中,仅仅是引用地址的传递。每个页面的array原生对象引用的地址是不一样的,在子页面中声明的array,所对应的构造函数,是子页面的array对象,在父页面进行判断时,使用的并不是子页面的array。
十、数组占位
let array = Array(3).fill('');console.log(array); //["", "", ""]
十一、数组去重多重方式
11.1 Set(最常用)
Array.prototype.unique = function(){return [...new Set(this)];}vararray = [1, 2, 3, 43, 45, 1, 2, 2, 4, 5];array.unique();

11.2 Map
Array.prototype.unique = function() {const tmp = newMap();returnthis.filter(item => {return !tmp.has(item) && tmp.set(item, 1);})}var array = [1, 2, 3, 43, 45, 1, 2, 2, 4, 5];array.unique();

11.3 Array.prototype.indexOf()
Array.prototype.unique = function() {returnthis.filter((item, index) => {returnthis.indexOf(item) === index;})}var array = [1, 2, 3, 43, 45, 1, 2, 2, 4, 5];array.unique();
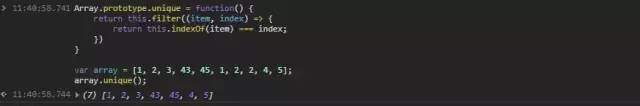
11.4 Array.prototype.includes()
Array.prototype.unique = function(){const newArray = [];this.forEach(item => {if (!newArray.includes(item)) {newArray.push(item);}});return newArray;}vararray = [1, 2, 3, 43, 45, 1, 2, 2, 4, 5];array.unique();

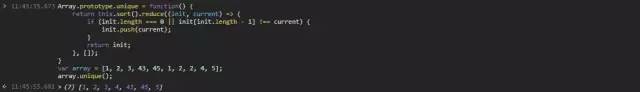
11.5 Array.prototype.reduce()
Array.prototype.unique = function() {returnthis.sort().reduce((init, current) => {if (init.length === 0 || init[init.length - 1] !== current) {init.push(current);}returninit;}, []);}var array = [1, 2, 3, 43, 45, 1, 2, 2, 4, 5];array.unique();
十二、短路运算(&& ||)
使用&&将返回第一个条件为假的值。如果每个操作数的计算值都为true,则返回最后一个计算过的表达式。
let one = 1, two = 2, three = 3;console.log(one && two && three); // 3console.log(0 && null); // 0
使用||将返回第一个条件为真的值。如果每个操作数的计算结果都为false,则返回最后一个计算过的表达式。
let one = 1, two = 2, three = 3;console.log(one || two || three); // 1console.log(0 || null); // null
十三、过滤空值
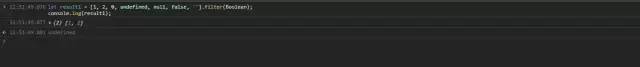
let result1 = [1, 2, 0, undefined, null, false, ''].filter(Boolean);console.log(result1);
十四、创建空对象
let dict = Object.create(null);十五、合并对象
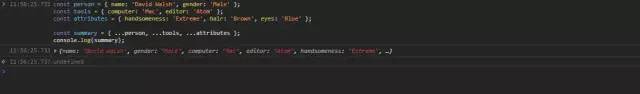
const person = { name: 'David Walsh', gender: 'Male' };const tools = { computer: 'Mac', editor: 'Atom' };const attributes = { handsomeness: 'Extreme', hair: 'Brown', eyes: 'Blue' };const summary = { ...person, ...tools, ...attributes };console.log(summary);
十六、字符串去空格
String.prototype.trim = function(){returnthis.replace(/^\s+|\s+$/g, "");};十七、对象转换为数组
var argArray = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);十八、逗号操作符
var a = 0;var b = ( a++, 99 );console.log(a);console.log(b);
十九、 localStorage.getItem('key') === localStorage.key
来源: 沉末_评论。
localStorage.setItem('item', 1);localStorage.getItem('item') === localStorage.item;

二十、从一堆文本中获取手机号
来源: 飞蛾扑火评论。
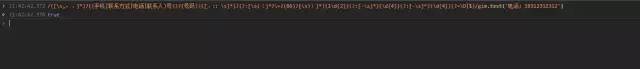
([\s,,、]*)?((手机|联系方式|电话|联系人)号?)?(号码)?([、::\s]*)?(?:[\s((]*?\+?(86)?[\s))]*)(1\d{2})(?:[-\s]*)(\d{4})(?:[-\s]*)(\d{4})(?=\D|$)
二十一、整数变量交换
来源: 快乐的仲子评论。
let a = 10;let b = 50;a = a ^ b;b = a ^ b;a = a ^ b;console.log(a, b); // 50 10

二十二、整数变量交换
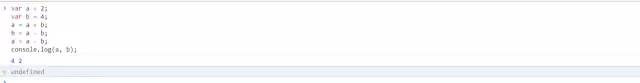
var a = 2;var b = 4;a = a + b;b = a - b;a = a - b;console.log(a, b); // 4 2
评论出你的“奇人异巧”,让大家都学习。
源自:https://juejin.im/post/5dd4a4015188252a18737535
评论
