Nacos12# 随机权重负载均衡算法
引言
Nacos在Client选择节点时提供了一种基于权重的随机算法,通过源码分析掌握其实现原理,方便实战中加以运用。
下面以图示的方式贯穿下随机权重负载均衡算法的流程:
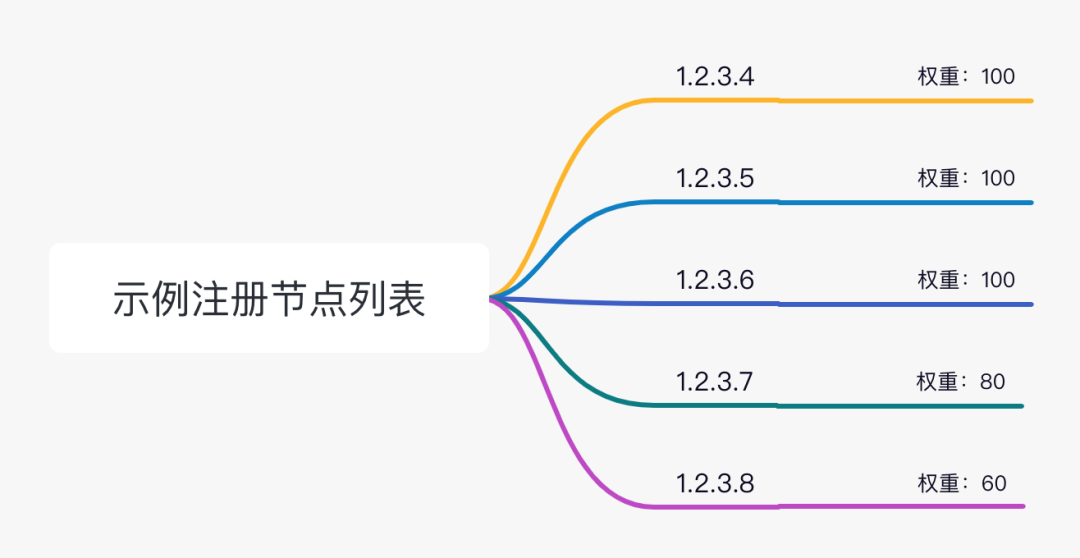
节点列表
假设注册了5个节点,每个节点的权重如下。
组织递增数组
目的在于形成weights数组,该数组元素取值[0~1]范围,元素逐个递增,计算过程如下图示。另外注意非健康节点或者权重小于等于0的不会被选择。
随机算法
通过生成[0~1]范围的随机数,通过二分法查找递增数组weights[]接近的index,再从注册节点列表中返回节点。

随机权重负载均衡算法是在NacosNamingService#selectOneHealthyInstance提供,一起走查下。
@Override
public Instance selectOneHealthyInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, boolean subscribe)
throws NacosException {
return selectOneHealthyInstance(serviceName, groupName, new ArrayList<String>(), subscribe);
}
@Override
public Instance selectOneHealthyInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, List<String> clusters,
boolean subscribe) throws NacosException {
String clusterString = StringUtils.join(clusters, ",");
// 注解@1
if (subscribe) {
ServiceInfo serviceInfo = serviceInfoHolder.getServiceInfo(serviceName, groupName, clusterString);
if (null == serviceInfo) {
serviceInfo = clientProxy.subscribe(serviceName, groupName, clusterString);
}
return Balancer.RandomByWeight.selectHost(serviceInfo);
} else {
// 注解@2
ServiceInfo serviceInfo = clientProxy
.queryInstancesOfService(serviceName, groupName, clusterString, 0, false);
return Balancer.RandomByWeight.selectHost(serviceInfo);
}
}
注解@1 已订阅「从缓存获取注册节点列表」,默认subscribe为true。
注解@2 从 「从服务器获取注册节点列表」
protected static Instance getHostByRandomWeight(List<Instance> hosts) {
NAMING_LOGGER.debug("entry randomWithWeight");
if (hosts == null || hosts.size() == 0) {
NAMING_LOGGER.debug("hosts == null || hosts.size() == 0");
return null;
}
NAMING_LOGGER.debug("new Chooser");
List<Pair<Instance>> hostsWithWeight = new ArrayList<Pair<Instance>>();
for (Instance host : hosts) {
if (host.isHealthy()) { // 注解@3
hostsWithWeight.add(new Pair<Instance>(host, host.getWeight()));
}
}
NAMING_LOGGER.debug("for (Host host : hosts)");
Chooser<String, Instance> vipChooser = new Chooser<String, Instance>("www.taobao.com");
// 注解@4
vipChooser.refresh(hostsWithWeight);
NAMING_LOGGER.debug("vipChooser.refresh");
// 注解@5
return vipChooser.randomWithWeight();
}
注解@3 非健康节点不会被选中,组装Pair的列表,包含健康节点的权重和Host信息
注解@4 刷新需要的数据,具体包括三部分:所有健康节点权重求和、计算每个健康节点权重占比、组织递增数组。
public void refresh() {
Double originWeightSum = (double) 0;
// 注解@4.1
for (Pair<T> item : itemsWithWeight) {
double weight = item.weight();
// ignore item which weight is zero.see test_randomWithWeight_weight0 in ChooserTest
// weight小于等于 0的将会剔除
if (weight <= 0) {
continue;
}
items.add(item.item());
// 值如果无穷大
if (Double.isInfinite(weight)) {
weight = 10000.0D;
}
// 值如果为非数字值
if (Double.isNaN(weight)) {
weight = 1.0D;
}
// 累加权重总和
originWeightSum += weight;
}
// 注解@4.2
double[] exactWeights = new double[items.size()];
int index = 0;
for (Pair<T> item : itemsWithWeight) {
double singleWeight = item.weight();
//ignore item which weight is zero.see test_randomWithWeight_weight0 in ChooserTest
if (singleWeight <= 0) {
continue;
}
// 每个节点权重的占比
exactWeights[index++] = singleWeight / originWeightSum;
}
// 注解@4.3
weights = new double[items.size()];
double randomRange = 0D;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
weights[i] = randomRange + exactWeights[i];
randomRange += exactWeights[i];
}
double doublePrecisionDelta = 0.0001;
if (index == 0 || (Math.abs(weights[index - 1] - 1) < doublePrecisionDelta)) {
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cumulative Weight caculate wrong , the sum of probabilities does not equals 1.");
}
注解@4.1 所有健康节点权重求和originWeightSum
注解@4.2 计算每个健康节点权重占比exactWeights数组
注解@4.3 组织递增数组weights,每个元素值为数组前面元素之和
以一个例子来表示这个过程,假设有5个节点:
1.2.3.4 100
1.2.3.5 100
1.2.3.6 100
1.2.3.7 80
1.2.3.8 60
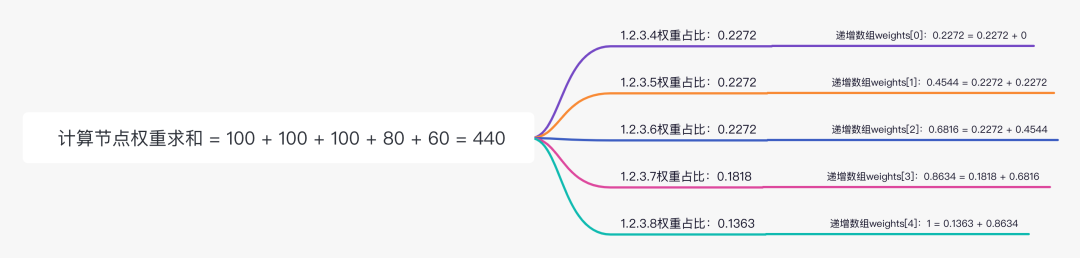
步骤一 计算节点权重求和
originWeightSum = 100 + 100 + 100 + 80 + 60 = 440
步骤二 计算每个节点权重占比
exactWeights[0] = 0.2272
exactWeights[1] = 0.2272
exactWeights[2] = 0.2272
exactWeights[3] = 0.1818
exactWeights[4] = 0.1363
步骤三 组织递增数组weights
weights[0] = 0.2272
weights[1] = 0.4544
weights[2] = 0.6816
weights[3] = 0.8634
weights[4] = 1
注解@5 随机选取一个,逻辑如下:
public T randomWithWeight() {
Ref<T> ref = this.ref;
// 注解@5.1
double random = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble(0, 1);
// 注解@5.2
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(ref.weights, random);
// 注解@5.3
if (index < 0) {
index = -index - 1;
} else {
// 注解@5.4
return ref.items.get(index);
}
// 返回选中的元素
if (index >= 0 && index < ref.weights.length) {
if (random < ref.weights[index]) {
return ref.items.get(index);
}
}
/* This should never happen, but it ensures we will return a correct
* object in case there is some floating point inequality problem
* wrt the cumulative probabilities. */
return ref.items.get(ref.items.size() - 1);
}
注解@5.1 产生0到1区间的随机数
注解@5.2 二分法查找数组中接近的值
注解@5.3 没有命中返回插入数组理想索引值
注解@5.4 命中直接返回选中节点
小结: 一种基于权重的随机算法的实现过程,扒开看也不复杂。
