如何在 C# 中使用隐式和显式操作符

C# 有一个鲜为人知的特性是通过定义 显式和隐式操作符 实现类型之间的转换,这篇文章我们将会讨论如何使用这些 显式 和 隐式 操作符。
什么是显式,什么是隐式
隐式类型转换 它是运行时自动帮你完成的,言外之意就是你不需要人为干预,比如下面的例子就是典型的 隐式类型转换。
int x = 100;
double d = x;
不过下面的代码则过不了编译器。
double d = 100.25;
int x = d;
编译程序时,将会出现下面的错误。
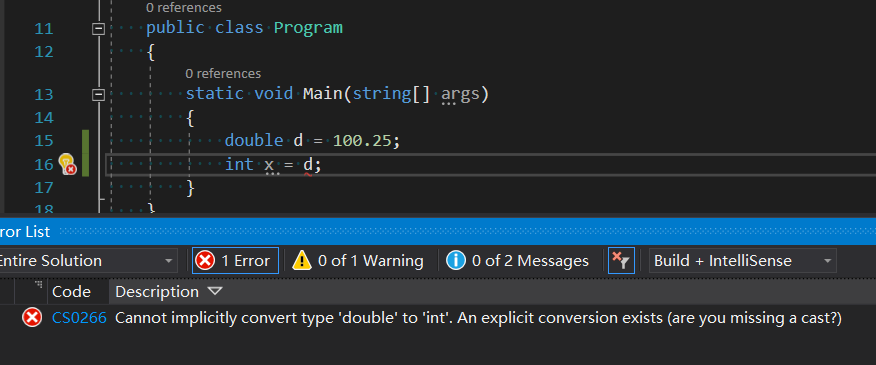
显而易见,上面的 double 不能隐式的转成 int,除非显式转换,那如何显式呢?可以使用如下代码。
int x = 100;
double d = (int) x;
人工干预后,编译器也就放行了。
创建 DTO 类
接下来我们研究一下如何在 用户自定义类型 上使用 隐式 和 显式转换,比如:Class,考虑下面的类。
public class Author
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
public class AuthorDto
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
在上面的代码中,定义了一个 Author 实体类,然后再为 Author 定义一个数据传输对象 AuthorDTO,数据传输对象是一个数据容器,常用于在 Presentation 和 Application层 之间传递数据。
Model 和 DTO 之间的相互转换
下面的代码展示了如何实现 Author 和 AuthorDto 之间的相互转换。
public AuthorDto ConvertAuthorToAuthorDto(Author author)
{
AuthorDto authorDto = new AuthorDto
{
Id = author.Id.ToString(),
FirstName = author.FirstName,
LastName = author.LastName
};
return authorDto;
}
public Author ConvertAuthorDtoToAuthor(AuthorDto authorDto)
{
Author author = new Author
{
Id = Guid.Parse(authorDto.Id),
FirstName = authorDto.FirstName,
LastName = authorDto.LastName
};
return author;
}
如果需要在应用程序中为若干个类写这样的转换代码,你会发现实现类之间的转换使的代码比较冗余,而且代码可读性也好不到哪里去。所以在这种场景下就是 显式 和 隐式 操作符的用武之地。
使用隐式操作符
实现 model-dto 之间的转换更简单粗暴的方式就是使用 隐显式操作符,这样就避免了冗长的方法调用,让代码更加的直截了当。
下面的代码展示了如何使用 隐式操作符 将 Author实例 转成 AuthorDto 实例。
public static implicit operator AuthorDto(Author author)
{
AuthorDto authorDto = new AuthorDto();
authorDto.Id = author.Id.ToString();
authorDto.FirstName = author.FirstName;
authorDto.LastName = author.LastName;
return authorDto;
}
接下来看一下如何在 Main 方法中使用 隐式操作符。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Author author = new Author();
author.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
author.FirstName = "Joydip";
author.LastName = "Kanjilal";
AuthorDto authorDto = author;
Console.ReadKey();
}
使用显式操作符
下面的代码展示了如何利用 显式操作符 将 Author 实例转成 AuthorDto 。
public static explicit operator AuthorDto(Author author)
{
AuthorDto authorDto = new AuthorDto();
authorDto.Id = author.Id.ToString();
authorDto.FirstName = author.FirstName;
authorDto.LastName = author.LastName;
return authorDto;
}
这时候在 Main 方法中就需要人工介入进行强转了,如下代码所示:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Author author = new Author();
author.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
author.FirstName = "Joydip";
author.LastName = "Kanjilal";
AuthorDto authorDto = (AuthorDto)author;
Console.ReadKey();
}
值得注意的是,你不能在一个类中的对象转换同时定义 显式 和 隐式操作符,如下图所示:
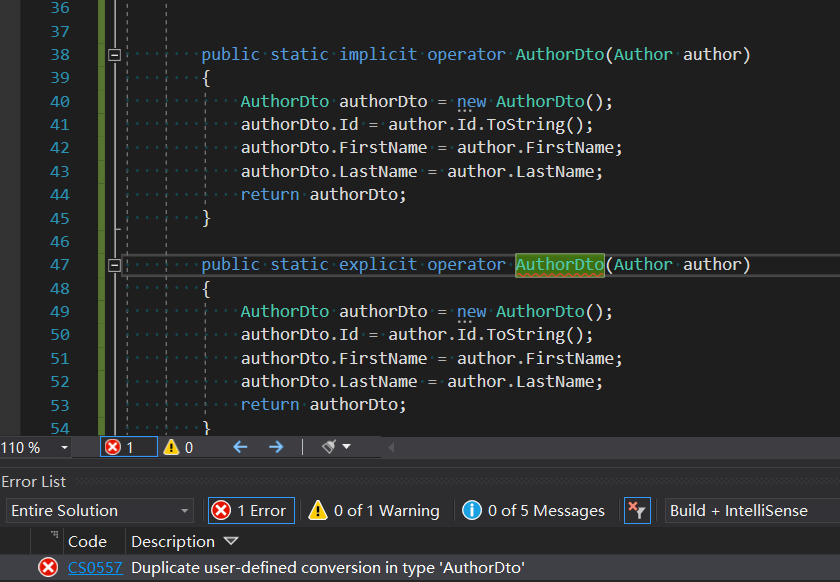
如果你定义了隐式操作符,那么对象之间的转换可以是隐式或显式,如果你定义了显式操作符,那么你只能显式的实现对象转换,虽然隐式操作使用起来非常方便,但显式操作会让代码意图更明显,可读性更高。
译文链接:https://www.infoworld.com/article/3606436/how-to-use-implicit-and-explicit-operators-in-csharp.html
.NET Core实战项目之CMS 第一章 入门篇-开篇及总体规划
【.NET Core微服务实战-统一身份认证】开篇及目录索引
Redis基本使用及百亿数据量中的使用技巧分享(附视频地址及观看指南)
.NET Core中的一个接口多种实现的依赖注入与动态选择看这篇就够了
用abp vNext快速开发Quartz.NET定时任务管理界面
